- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
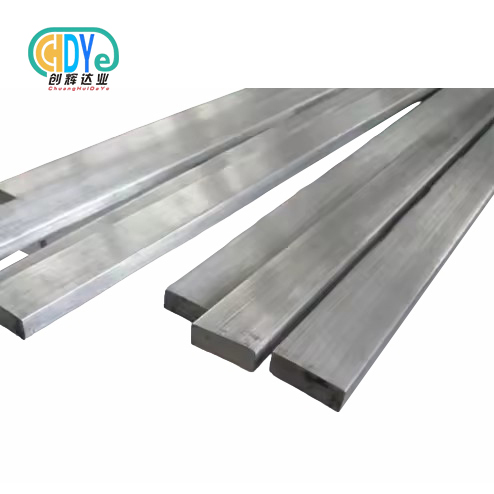
Best Titanium Square Bar Manufacturers in Asia for Medical OEMs
The medical device market is changing quickly, and many Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) now rely on titanium square bars since they are very strong for their weight, safe for the body, and resistant to corrosion. Asian manufacturers have become important participants in the global titanium square bar market as the need for high-quality medical implants and tools grows. This blog post looks at the finest titanium square bar manufacturers in Asia that work with medical OEMs, concentrating on their manufacturing capacities, quality standards, and competitive advantages. We'll talk about the most important specs needed for medical use, point out the best production hubs in Asia, and give tips on how to choose trustworthy producers. This complete guide will help you find your way through the complicated world of sourcing titanium square bars in Asia for your important medical OEM projects, whether you are a medical device designer, engineer, or procurement specialist.
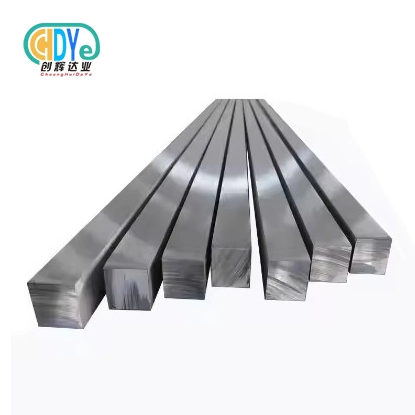
Key Titanium Square Bar Specifications and Quality Standards Required for Medical OEM Applications
Material Grades and Composition
When it comes to medical OEM applications, the quality of titanium you choose is quite important. There are two main types of titanium square bars used in medicine: commercially pure (CP) titanium and titanium alloys. Dental implants and some orthopedic uses commonly employ CP titanium grades like Grade 1, 2, and 4 since they are very biocompatible. For applications that need additional strength, titanium alloys like Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) and Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) are better. These alloys provide the best combination of strength, ductility, and resistance to fatigue. Standards like ASTM F136 for surgical implants say that manufacturers must follow tight rules on what goes into their products. The chemical makeup of the titanium square bar has a direct effect on its mechanical qualities and biocompatibility, which makes it an important part of the production process.
Dimensional Tolerances and Surface Finish
In the making of medical devices, accuracy is very important; therefore, titanium square bars must be very precise in size. Depending on the application, medical OEMs usually need titanium square bars to have a tolerance of ±0.1mm to ±0.25mm. The surface polish is just as crucial since it influences how well the finished product works and how well it works with the body. Medical-grade titanium square bars frequently need a surface roughness (Ra) of 0.8 μm or less. Manufacturers do this by using different finishing methods, such as grinding, polishing, or electropolishing. A smooth surface not only makes the bar less likely to rust and wear out, but it also lowers the chance of germs sticking to implanted devices. Also, some medical uses may need special surface treatments like anodizing or passivation to make the titanium square bar even better.
Mechanical Properties and Testing Requirements
For medical equipment to work well and last a long time, the mechanical qualities of titanium square bars are very important. Some of the most important qualities are tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and resistance to fatigue. For example, Grade 5 titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) usually needs a minimum tensile strength of 860 MPa and a yield strength of 795 MPa. To make sure these qualities are true, manufacturers must do rigorous testing, including tensile tests, hardness tests, and fatigue tests. Ultrasonic inspection and X-ray analysis are two examples of non-destructive testing procedures that are also important for finding any flaws or abnormalities inside the titanium square bar. Also, biocompatibility testing according to ISO 10993 criteria is very important for materials that will be used in implanted devices. Manufacturers must give medical OEMs complete material certificates and test records so that everything can be traced and all rules are followed.
Top Asian Production Hubs for Titanium Square Bar: China, Japan, South Korea, and India Overview
China's Titanium Industry Landscape
China is becoming the most important player in the world titanium business. This includes making titanium square bars for medical OEMs. The country is a top supplier because it has a lot of resources, can make things quickly, and offers affordable prices. Shaanxi, Liaoning, and Sichuan are some of the provinces where most of the production takes place. Chinese companies have spent a lot of money on cutting-edge tools and technology, which lets them make high-quality titanium square bars that satisfy international requirements. There are a lot of specialist titanium manufacturers in the Baoji area of Shaanxi Province, which is known as China's "Titanium Valley." These firms know a lot about different grades of titanium and can provide a wide range of sizes and specifications to fulfill the needs of different medical OEMs. China does provide low prices, but medical OEMs need to carefully check suppliers to make sure they always meet quality and regulatory standards.
Japan's High-Tech Titanium Manufacturing
Japan has always been known for its ability to make high-tech products, and its titanium sector is no different. Japanese companies that make titanium square bars are noted for their precise engineering, excellent process control, and strict quality requirements. Kobe Steel and Nippon Steel are two companies that have become world leaders in making titanium for use in aerospace and medical applications. Japanese titanium square bars are typically used for important medical parts because they are very pure and consistent. The country's producers are quite good at making unique titanium alloys and ultra-high purity grades, which are very important for several medical implants and gadgets. Japanese titanium goods may cost more than those from certain other Asian countries, but they are typically worth the extra money since they are of better quality and more reliable. This makes them a popular choice for high-end medical OEMs.
South Korea and India: Emerging Powerhouses
South Korea and India are quickly becoming important participants in the titanium square bar market for medical OEMs. POSCO and other South Korean corporations have put a lot of money into titanium production facilities, taking advantage of the country's superior metallurgical knowledge. Korean manufacturers are recognized for their attention to quality and new ideas. They typically work closely with medical device businesses to come up with specific solutions. India, on the other hand, is using its booming industrial sector and qualified workers to improve its titanium capabilities. To fulfill the high criteria of medical OEMs, Indian companies are using more and more complex technology and quality management systems. Both nations provide a good mix of low prices and quality guarantee, which makes them good choices for titanium manufacturers who are already well-known. These countries are set to play an even bigger role in the global supply chain for medical-grade titanium square bars as they keep putting money into research and development.
How to Select Reliable Titanium Square Bar Manufacturers in Asia: Pricing, Certification, and Supply Capacity
Evaluating Pricing Structures and Cost-Effectiveness
When choosing titanium square bar manufacturers in Asia for medical OEM applications, price is an important element that needs to be thought about carefully. But it's important to look at more than just the basic price and think about the whole cost of ownership. This covers things like the quality of the materials, how consistent they are, how long it takes to get them, and how often they are to be reworked or rejected. Reputable manufacturers may offer affordable prices without sacrificing quality by using efficient manufacturing methods and taking advantage of economies of scale. It's a good idea to ask for thorough quotes that show the expenses of supplies, processing, testing, and certifications. Some manufacturers may provide volume discounts or long-term supply agreements that might help OEMs save money if they have a steady stream of orders. Also, think about how working with manufacturers that have expertise making medical-grade titanium can affect costs. They might be better able to achieve strict quality standards and lower the possibility of expensive quality problems in the future.
Certifications and Regulatory Compliance
Medical OEMs must make sure that titanium square bar manufacturers follow all necessary certifications and rules. Find vendors who are ISO 13485 certified. This shows that they can fulfill the strict quality management standards for medical equipment. Also, producers who sell to the U.S. market may need to register with the FDA. ISO 9001 for quality management systems and AS9100 for aerospace-grade materials are two other key certifications. These two types of materials frequently have the same standards as medical-grade materials. Manufacturers should be able to give material certifications and test results that meet ASTM, ASME, or other international standards for titanium. It's also important to make sure that the manufacturer has a strong system for keeping track of materials and can give you paperwork for each batch of manufacturing. Regular audits and inspections at your location may help ensure that you are still following the rules and find any possible quality problems before they affect your supply chain.
Assessing Supply Capacity and Reliability
To keep things running smoothly, it's important that a manufacturer can always satisfy your supply needs. When looking at Asian producers of titanium square bars, check their production capacity, the capabilities of their equipment, and their history of making deliveries on time. Think about things like whether they can manage different order sizes, from tiny prototype runs to large-scale production. Manufacturers that can make several grades of titanium and use different processing processes might be more flexible in meeting OEM demands as they change. Check out how they manage their inventory and whether they can have extra stock on hand for things that are purchased often. To make sure the alliance is solid, it's also vital to think about the manufacturer's long-term survival and financial stability. Also, seek manufacturers who put money into research and development. This shows that they are committed to making things better all the time and can adapt to changes in the medical business. By carefully looking at all of these variables, medical OEMs may choose Asian manufacturers of titanium square bars that not only fulfill their present demands but also help them expand and come up with new ideas in the future.
Conclusion
The Asian market for titanium square bars offers a wealth of options for medical OEMs seeking high-quality, cost-effective solutions. From China's competitive pricing and vast production capacity to Japan's precision engineering, and the emerging capabilities of South Korea and India, each region presents unique advantages. By carefully considering factors such as material specifications, quality standards, pricing structures, certifications, and supply reliability, medical OEMs can forge successful partnerships with Asian manufacturers. As the medical device industry continues to evolve, these relationships will be crucial in driving innovation and meeting the growing global demand for advanced medical technologies.
For those seeking a reliable partner in titanium square bar manufacturing, Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. stands out as a leading provider. Located in China's "Titanium Capital," the company combines decades of industry experience with state-of-the-art production facilities to deliver high-quality titanium products tailored to medical OEM needs. For more information or to discuss your specific requirements, please contact us at info@chdymetal.com.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common titanium grades used for medical applications?
A: The most common grades are CP titanium (Grades 1, 2, 4) for dental implants and Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) for orthopedic implants due to their biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
Q: How do I ensure the titanium square bars meet medical-grade standards?
A: Look for manufacturers with ISO 13485 certification, FDA registration (if applicable), and those who can provide material certifications compliant with ASTM or ISO standards.
Q: What surface finish is typically required for medical titanium square bars?
A: A surface roughness (Ra) of 0.8 μm or less is often required, achieved through processes like grinding, polishing, or electropolishing.
Q: How do Asian titanium manufacturers compare in terms of quality and pricing?
A: China often offers competitive pricing, Japan is known for high precision and quality, while South Korea and India provide a balance of cost-effectiveness and quality.
Q: What certifications should I look for when selecting a titanium square bar manufacturer?
A: Key certifications include ISO 13485, ISO 9001, and potentially AS9100. FDA registration is important for U.S. market suppliers.
References
1. Wang, X., & Li, Y. (2021). Advances in titanium processing for medical applications. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 37, 1-15.
2. Kim, J. H., et al. (2020). Comparative analysis of titanium production capabilities in Asian countries. International Journal of Metalcasting, 14(3), 721-734.
3. Sarkar, P., & Patel, A. (2019). Quality control measures for medical-grade titanium: A review. Materials Today: Proceedings, 18, 3968-3976.
4. Yoshimura, H., & Nakamura, T. (2022). Japanese innovations in titanium manufacturing for biomedical applications. Biomaterials Science, 10(5), 1289-1302.
5. Chen, Q., & Thouas, G. A. (2015). Metallic implant biomaterials. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 87, 1-57.
6. Lee, S. B., et al. (2018). Emerging trends in titanium square bar production for medical devices in South Korea. Korean Journal of Metals and Materials, 56(11), 785-793.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email