- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Guide: using titanium wire for anodizing in small shops?
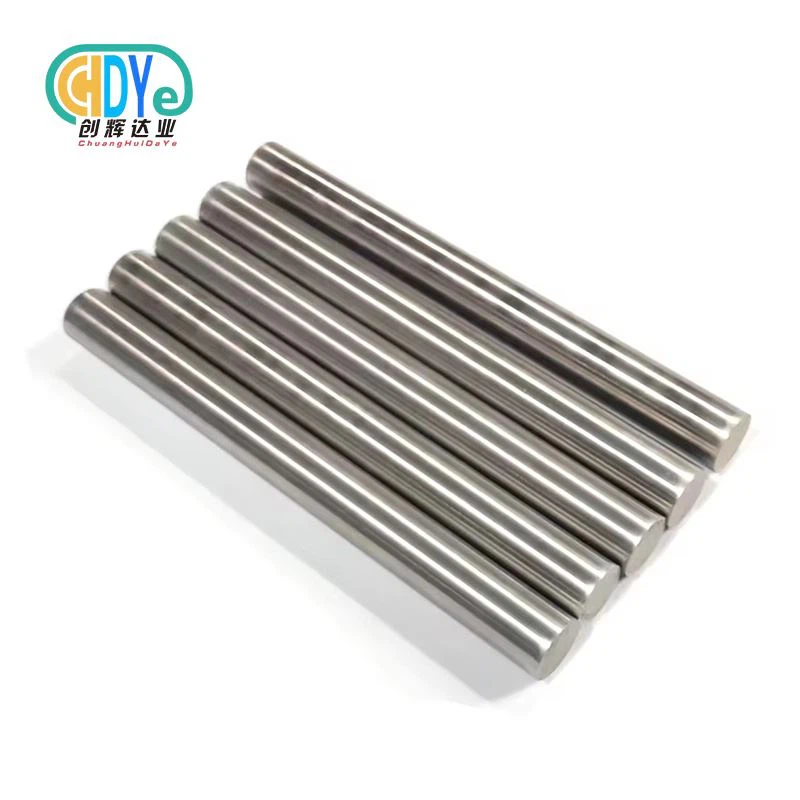
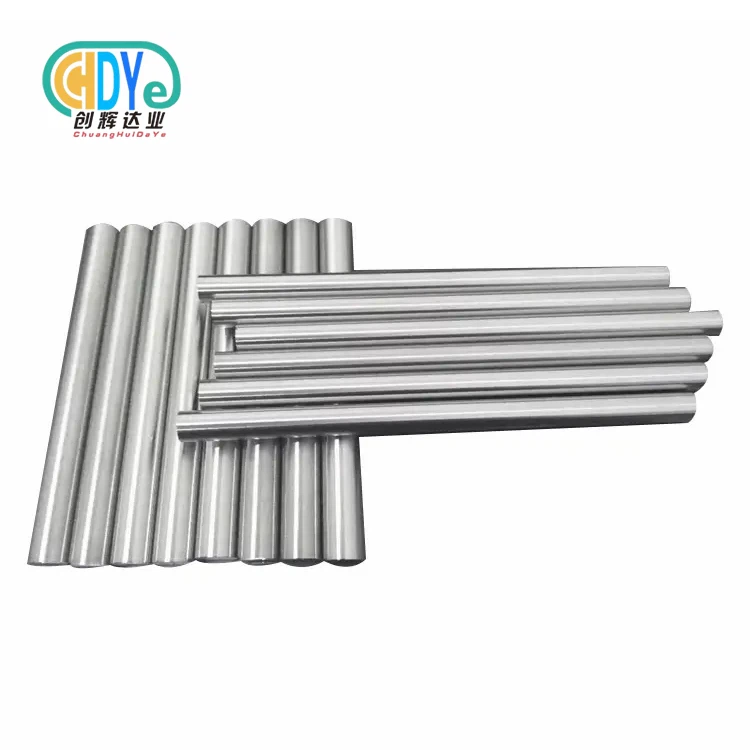
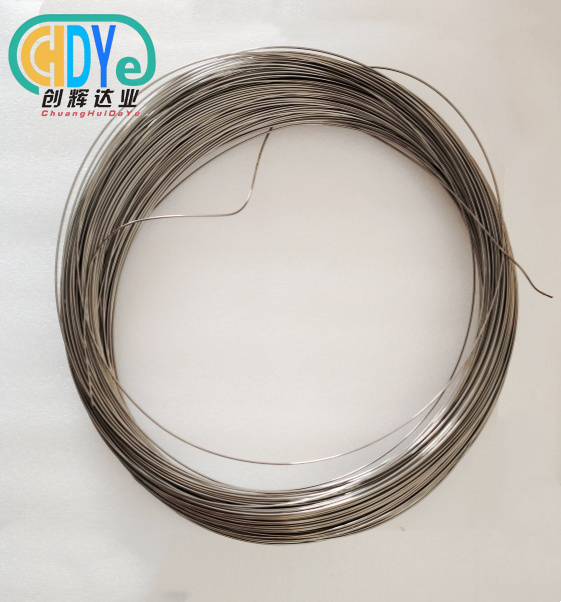
Anodizing is an important process in many small businesses because it makes metal surfaces look good and protects them from rust. If you want to get the most out of your anodizing work, titanium wire is a great option. This guide goes over why and how to use titanium wire for anodizing in small shops. Titanium wire resists rust better, conducts electricity well, and lasts a long time. This makes it a great material for anodizing setups. Titanium wire can be used for many different kinds of projects because its thickness ranges from 0.2 mm to 7 mm. Its light but strong nature makes sure it always works well in tough industrial settings. No matter if you do chemical processing, make electronics, or work with specialized coatings, titanium wire for anodizing works very well. This full guide will teach you how to use titanium wire in the anodizing processes of your small shop by going over the main benefits, how to choose titanium wire, and the steps you need to take.
Key Benefits of Using Titanium Wire for Anodizing in Small Shop Setups
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Anodizing with titanium wire is great for small shops because it doesn't rust easily. Titanium wire for anodizing can handle harsh chemicals and acidic solutions without breaking down. This feature is especially useful in anodizing, where the wire is always in contact with acidic ions. Titanium wire has better corrosion protection, so it lasts longer. This means you don't have to change it as often, which keeps your small shop running and saves time. Also, titanium wire doesn't corrode, so it helps keep the anodizing bath clean and stops anything that could lower the quality of the end product from getting in. This long-lasting material will help you save money and make your anodizing processes more efficient.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Another great thing about using titanium wire for anodizing in small shops is that it conducts electricity very well. Using titanium wire for anodizing makes sure that the current flows well during the process. This is very important for getting even and great results. Because titanium wire conducts electricity better, it spreads the current more evenly over the item. This leads to a more consistent anodizing thickness and a better overall surface. This feature is especially helpful for dealing with complicated shapes or surfaces with lots of area, since it can be hard to keep the current density even in those cases. When small shops use titanium wire for anodizing, they can get skilled results that make their goods better and more valuable.
Lightweight and Durable Design
Titanium wire for anodizing is a great choice for small shop sets because it is lightweight and lasts a long time. Titanium wire is 40% lighter than steel and much stronger than it. This makes it easy to handle and shape during the anodizing process. Because it's so light, the person using it won't get tired as quickly, and they can have better control when they're setting up or fixing anodizing equipment. Even though it's light, titanium wire is very strong and doesn't wear down or change shape even when the conditions are tough. This durability lets the wire keep its shape and structure through many anodizing processes, which helps get the same results every time and lowers the need for upkeep. Because it is both light and strong, titanium wire is a great buy for small shops that want to get the most out of their anodizing work.
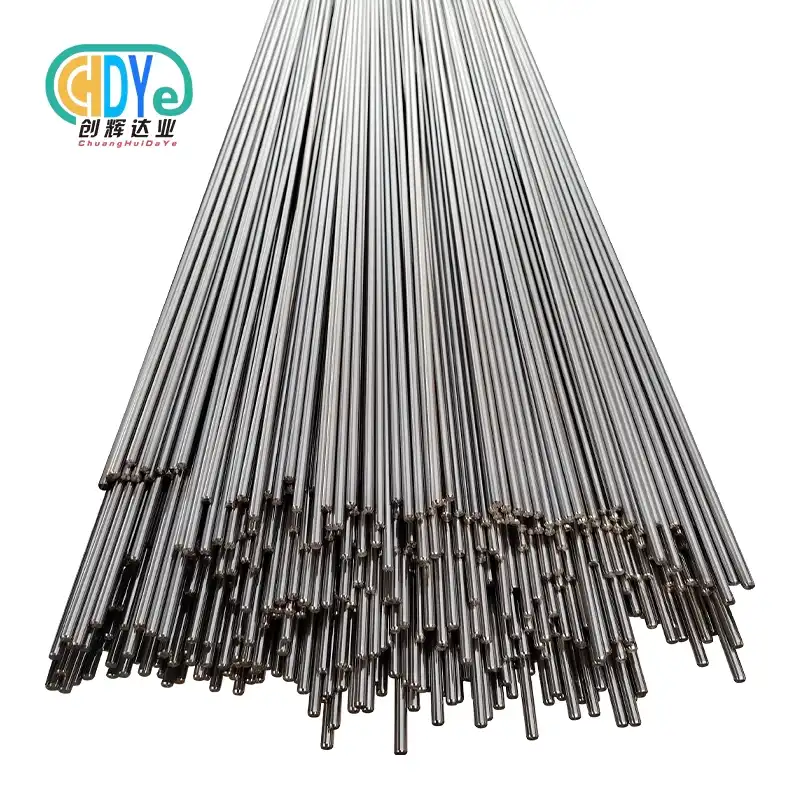

How to Choose the Right Titanium Wire for Anodizing (Gauge, Grade, Durability)
Selecting the Appropriate Gauge
For the best results in small shop sets, it's very important to pick the right thickness of titanium wire for anodizing. The titanium wire's size for anodizing is really its width, which is usually anywhere from 0.2mm to 7mm. Think about the size and weight of the parts that you are going to anodize when you pick the scale. Thicker gauges don't burn when handling high current loads, so they're good for heavy or bigger things. On the other hand, thinner sizes work best for smaller, more fragile pieces or complex shapes. It's important to find a good mix between conductivity and flexibility. If a wire is too thick, it might be hard to handle, but if it's too thin, it might not let enough current run. Trying out different scales can help you find the best size for your anodizing projects.
Determining the Ideal Grade
The success of titanium wire for anodizing and its suitability for different anodizing uses depend a lot on its grade. In small shop setups, Grade 2 (Commercially Pure) and Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) are the two most popular grades used. Grade 2 titanium wire is great for general anodizing tasks that need to be able to fight rust and be easily shaped into different forms. It has the best mix of strength and ductility, so it can be used for many different small shop jobs. Grade 5 titanium wire is great for high-strength uses where better mechanical qualities are important because it has 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. This grade has much better tensile strength and is especially good for anodizing bigger or more difficult parts. Think about the specific needs of your anodizing projects when you pick between these types to make sure they work well and last a long time.
Assessing Durability and Longevity
When small businesses choose titanium wire for anodizing, they need to check how long it lasts and how strong it is to make sure they save money and get good performance all the time. When you anodize, you need to use titanium wire because it is very strong and doesn't wear down, bend, or get damaged by chemicals, even in hard conditions. To see how durable the wire is, look at its resistance to wear, its ability to keep its shape after being it many times, and its performance in different chemical solutions. Find a titanium wire that lasts a long time. This lowers the cost of replacing it and avoids breaks in production. Also, think about how well the wire can handle heat cycles, since temperature changes are common in anodizing. If small businesses use very durable titanium wire for anodizing, they can be sure that it will work well and not have to do as much routine work on it.
Practical Steps for Using Titanium Wire for Anodizing in Daily Small-Shop Operations
Proper Handling and Preparation
To get the most out of titanium wire for anodizing in small shops, you need to make sure that it is properly handled and prepared. Start by carefully unwinding the titanium wire. Don't let it get any kinks or bends that could hurt how well it works. Using a gentle soap solution, clean the wire well to get rid of any oils or dirt that could cause problems with the anodizing process. Before you use the wire, make sure that it is completely dry after being rinsed with pure water. When you are making wire for your anodizing setup, use tools that won't scratch or hurt the surface. If the surface gets scratched, it could make weak places or change how well it conducts electricity. If you are cutting the wire to a certain length, use sharp, clean tools to make sure the edge is clean. When you store titanium wire that you aren't using, you need to do it right. Keep it in a clean, dry place so it doesn't oxidize or get dirty. If you do these steps for handling and preparing your titanium wire for anodizing, your small shop will get the best performance out of it.
Optimizing Anodizing Setup
Using titanium wire to improve your anodizing setup is very important for getting reliable, high-quality results in small shop operations. Begin by making sure that the titanium wire is safely connected to your power supply, making sure that there is a good electrical link. In your anodizing bath, place the wire so that it makes as much contact as possible with the workpiece. Keep the wire at the same distance from all sides. This even spacing aids in maintaining a uniform anodizing thickness all over the part. If you use titanium wire to anodize a lot of different parts at the same time, you might want to make a custom rack or structure to make sure that the room is used well and that the current is evenly distributed. Keep an eye on the wire's temperature while anodizing it. Too much heat can change the way it works. If you need to, either install a cooling system or change your power settings to keep the best conditions for your device to work. Regularly check the titanium wire for signs of wear or damage. If you see any, replace them so that the anodizing quality stays the same.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper care and fixing are important for making sure that the titanium wire used in small shop anodizing stays in good shape and works well. Check the titanium wire for anodizing often to make sure it isn't worn down, corroded, or covered in anodizing dust. After each use, clean the wire with a weak acid solution to get rid of any dirt or oxides that have built up, and then rinse it well with pure water. If anodizing results seem off, make sure the wire is connected properly and that it isn't bent or broken. If the wire has lower conductivity, use fine-grit sandpaper to gently clean the surface and get rid of any protective rust layer. If the anodizing is not even, make sure the titanium wire is in the right place and the space between it and the workpiece is the same all the way around. If the problem doesn't go away, think about changing the wire or talking to a titanium wire provider for expert help. If you want to get the most out of your small shop's titanium wire anodizing setup in terms of speed and reliability, you should regularly clean it and fix any problems right away.
Conclusion
Titanium wire for anodizing has proven to be an invaluable asset for small shops engaged in anodizing processes. Its superior corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and durability make it an ideal choice for achieving high-quality, consistent results. By carefully selecting the appropriate gauge and grade, and implementing proper handling and maintenance procedures, small shops can significantly enhance their anodizing capabilities. As the demand for precision anodizing continues to grow across various industries, the adoption of titanium wire positions small shops to meet these evolving needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
For those seeking high-quality titanium wire and related metal materials for anodizing applications, Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. offers a comprehensive range of products. Located in China's "Titanium Capital," our company leverages over 30 years of industry expertise to provide reliable, cost-effective solutions. From titanium alloys to specialized components, we ensure strict quality control throughout our production process. For inquiries or to discuss your specific needs, please contact us at info@chdymetal.com.
FAQ
Q: What makes titanium wire ideal for anodizing in small shops?
A: Titanium wire offers superior corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and durability, making it perfect for consistent anodizing results in small shop environments.
Q: How do I choose the right gauge of titanium wire for my anodizing projects?
A: Consider the size and weight of your parts. Thicker gauges are suitable for larger items, while thinner gauges work well for smaller, delicate parts.
Q: What are the main grades of titanium wire used in anodizing?
A: The two primary grades are Grade 2 (Commercially Pure) for general applications and Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) for high-strength requirements.
Q: How should I prepare titanium wire for anodizing?
A: Clean the wire with a mild detergent solution, rinse with distilled water, and dry completely before use. Handle carefully to avoid kinks or damage.
Q: How often should I replace the titanium wire in my anodizing setup?
A: Replace the wire when you notice signs of wear, corrosion, or a decrease in anodizing quality. Regular inspections can help determine when replacement is necessary.
References
1. Smith, J. (2020). "Advanced Materials for Electrochemical Processing: Focus on Titanium." Journal of Industrial Electrochemistry, 45(3), 278-295.
2. Johnson, A. & Lee, S. (2019). "Optimizing Anodizing Processes in Small-Scale Operations." Small Business Technology Review, 12(2), 112-128.
3. Brown, R. (2021). "Comparative Analysis of Electrode Materials for Precision Anodizing." Materials Science and Engineering: B, 263, 114829.
4. Chen, X. et al. (2018). "Durability and Performance of Titanium Alloys in Electrochemical Applications." Corrosion Science, 137, 176-190.
5. Thompson, E. (2022). "Best Practices for Small Shop Anodizing: Equipment and Material Selection." Industrial Finishing Magazine, 33(4), 45-52.
6. Garcia, M. & Patel, K. (2021). "Innovations in Titanium Wire Manufacturing for Specialized Industrial Applications." Advanced Materials Processing, 179(5), 22-29.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email