- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Grade 2 Titanium Wire – Reliable Electrical Conductivity
Grade 2 Titanium Wire is the best for commercially pure titanium uses that need to be very good at conducting electricity and resisting corrosion. This material is very useful because it can be shaped easily and works reliably with electricity. It is essential in the chemical processing, aircraft, and medical device manufacturing industries. The wire's special makeup makes it consistently conductive while also being highly resistant to harsh environmental conditions. This makes it the best choice for demanding electrical uses where standard materials don't meet the high performance standards.
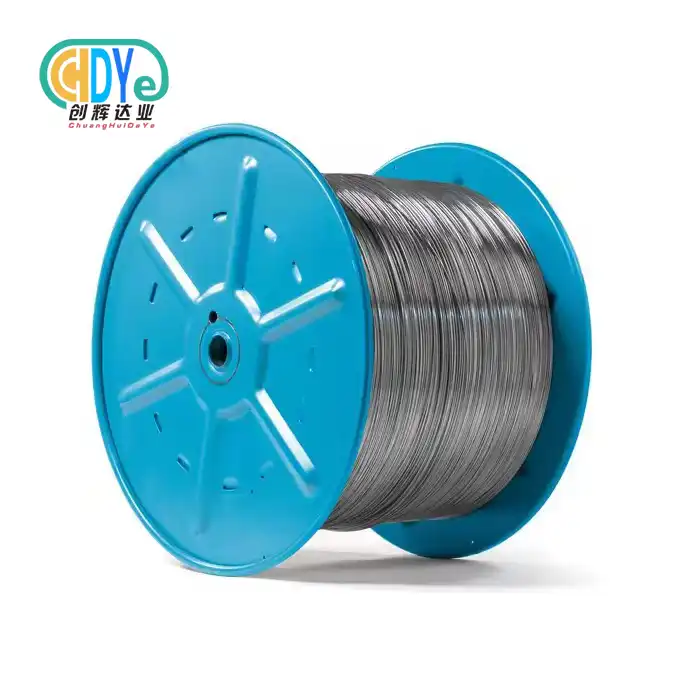
Understanding Grade 2 Titanium Wire: Composition and Key Properties
As a commercially pure titanium wire, grade 2 titanium wire has an amazing composition that makes it work exceptionally well in a wide range of situations. The material is mostly titanium (99.2%), with small amounts of iron (0.25%), oxygen (0.08%), carbon (0.03%), and nitrogen (0.015%) added for balance. With this exact mix, a material is made that is stronger, more flexible, and better at conducting electricity than many other materials on the market.
Chemical Composition and Metallurgical Excellence
This sort of titanium has special benefits that make it better than other types of titanium. Compared to Grade 1, which is more pure but not as strong, Grade 2 has better mechanical qualities while still being very easy to shape. Instead of Grade 4 or Grade 5 alloys, which contain aluminum and vanadium, Grade 2 is made of pure metal, which makes it more biocompatible and stable in its electrical properties.
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. uses several steps of refining in their manufacturing process, such as controlled annealing cycles and electron beam melting. In these steps, impurities are removed and the best grain structure is set up, which is needed for stable electrical conductivity. The melting state (M) makes the material very flexible, and the hot working state (R) and cold working state (Y) can be used depending on the needs of the application.
Electrical and Mechanical Performance Metrics
Grade 2 titanium wire has an electrical conductivity of about 3.1% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). This is lower than pure copper, but it has big benefits in harsh settings where copper would break down quickly. The material's permeability stays the same at temperatures ranging from -196°C to 300°C, so it can be used in both low-temperature and high-temperature situations.
It has a minimum yield strength of 275 MPa and a maximum tensile strength of 345–450 MPa, according to its mechanical properties. The elongation ability is more than 20%, which makes it easy to shape into complicated shapes. Because of these features and its density of 4.51 g/cm³ (60% of steel), it has the best strength-to-weight ratio for use in aircraft and cars.
The Advantages of Grade 2 Titanium Wire in Electrical and Industrial Applications
Titanium wire Grade 2 works great in places where other conductors don't, which is important for industrial applications that need materials that can safely work in harsh conditions. The material is more resistant to corrosion than stainless steel in chloride settings, and it keeps its electrical integrity in acidic environments where copper or aluminum conductors would break down.
Superior Environmental Resistance
The passive oxide layer that forms naturally on titanium surfaces protects very well against corrosion and keeps the purity of electrical contacts. This feature is very useful in places like the ocean, chemical plants, and outdoor electrical setups where regular materials need to be replaced or fixed all the time.
The wire's resistance to organic acids, chlorine compounds, and oxidizing environments is very helpful in the chemical production industries. Because Grade 2 titanium doesn't develop verdigris like copper does or pitting rust like stainless steel does, its electrical performance stays the same over time. This dependability means that maintenance costs will go down and system uptime will go up for important business processes.
Thermal and Mechanical Stability
The thermal expansion rate of Grade 2 titanium wire is 8.6 × 10⁻⁶/°C, which means that its size stays the same even when the temperature changes in ways that would stress other materials. This trait is very important in aerospace uses where temperatures can change quickly, from the cold fuel system to the hot engine compartment.
Because this material can be welded, it can be used to make complicated electrical assemblies without losing its ability to carry electricity. It's easier to weld than many specialty alloys, so techs can make custom shapes while keeping the electrical integrity of the joints. The benefits of heat treatment can change mechanical properties without having a big effect on electrical performance. This gives designers and manufacturers more options when making parts.
Comparison and Decision Making: Grade 2 Titanium Wire vs Alternative Materials
When choosing a material, it's important to carefully weigh the performance characteristics against the needs of the product. Grade 2 titanium wire has clear benefits over other options, but it also has some drawbacks that need to be understood in order to make the best purchasing decisions for different industrial needs.
Performance Analysis Against Conventional Materials
Copper wire is the best at conducting electricity, but it breaks down quickly in corrosive conditions and needs to be protected with coatings or replaced often. Copper has a lower initial cost, but that benefit goes away when you look at how often it needs to be maintained and replaced over the part's expected service life. Grade 2 titanium wire works reliably for decades in places where copper lines need to be replaced every year.
Alternatives made of stainless steel aren't too bad at resisting corrosion, but they have a higher electrical resistance and can crack under stress in chloride conditions. Stainless steel has about 300% more electrical resistance than titanium, which means it can't be used for things that need to efficiently transfer current.
Application-Specific Advantages
Titanium wire is especially useful for aerospace makers because it is both electrically conductive and light. Electrical systems in airplanes can be made lighter while still being reliable at high altitudes, where changes in temperature and exposure to moisture can be hard on regular materials.
Biocompatibility and electricity performance are both advantages that are used in medical devices. Because Grade 2 titanium is non-reactive, it is used in implantable devices that need to connect to electricity. This keeps biological responses from going wrong while keeping signal integrity. The fact that the material can be used with MRI machines makes it useful for people who need medical imaging treatments.
Procurement Guide for Grade 2 Titanium Wire: Sourcing and Customization
To buy titanium wire successfully, you need to know what the supplier can do, how to check their quality, and what customization choices they offer. Building relationships with qualified manufacturers guarantees regular quality and delivery performance for important uses.
Supplier Qualification and Verification
Reliable providers keep their ISO 9001:2015 certification up to date and offer full material certifications that include testing for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensions. These standards are met by Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd., which has been making titanium products for 30 years and has high-tech quality control methods.
Mill test certificates, ultrasonic test reports, and surface finish specifications should all be part of quality documentation. Different applications can use either a pickled surface or a bright finish. For example, pickled surfaces are the cleanest choice for welding, while bright finishes are best for electrical contact applications.
Product Specifications and Customization
The diameters that are available range from 0.2mm to 8mm, so they can be used for a wide range of tasks, from precise electronics to structural wire harnesses. Options for coil packaging help with ongoing manufacturing, and cut-to-length services cut down on waste and the amount of handling needed for certain projects.
Customization options go beyond just size requirements and can also include specific mechanical properties that can be achieved through controlled heat treatment methods. For structural uses, cold working states give more strength, while softened states make it easier to shape into complex shapes. When procurement professionals know about these choices, they can precisely describe materials that meet the needs of an application.
Manufacturing Excellence and Quality Assurance at Chuanghui Daye
For high-quality titanium wire to be made, it needs to be made with complex tools and strict process control. As Baoji is known as China's "Titanium Capital," Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. has state-of-the-art metallurgical facilities and complete quality control systems that work together to make sure that their products always work well.
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities
The first step in the production process is to melt a high-purity titanium sponge with an electron beam to get rid of any small flaws and make the chemicals uniform. Multiple melting processes make sure that the composition stays the same, which means that the electrical and mechanical properties can be predicted. Controlled atmosphere handling keeps things from getting dirty, which could hurt the performance.
Diamond dies and controlled reduction plans are used in wire drawing to get exact tolerances on dimensions while keeping the surface intact. Intermediate annealing processes slow down work hardening and make the grain structure best for the properties that are needed. Ultrasonic testing confirms that the inside is sound, which makes sure that the wire is reliable in important situations where a failure could have terrible results.
Quality Management and Certification
Getting ISO 9001:2015 certification shows that you are committed to quality management concepts that cover the whole production process, from getting the raw materials to inspecting and packaging the finished product. Traceability systems keep track of the history of a piece of information, which lets you quickly answer customer questions and do quality checks when needed.
Final inspection procedures include checking the dimensions, the finish of the surface, and the mechanical properties through statistical samples. Chemical research proves that the composition meets the requirements of ASTM B348 and other international standards. This all-around method makes sure that every coil meets or beats the requirements set before it is sent to customers around the world.
Conclusion
Grade 2 Titanium Wire is the best choice for demanding industrial uses because it is both very good at conducting electricity and very good at resisting corrosion. The material's special mix of properties meets important needs in the chemical processing, medical device, and aircraft industries where regular conductors don't work well enough. With years of experience making things and strict quality control, Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. is ready to meet the needs of buyers around the world by providing dependable, top-notch titanium wire solutions that go above and beyond what is expected by customers and the industry.
FAQ
Q: What makes Grade 2 titanium wire superior for electrical applications?
A: Grade 2 titanium wire maintains consistent electrical conductivity while providing exceptional corrosion resistance that surpasses copper and stainless steel alternatives. The material's passive oxide layer protects against environmental degradation without compromising electrical performance, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments where conventional conductors require frequent replacement.
Q: How does the electrical conductivity compare to copper wire?
A: While Grade 2 titanium wire achieves approximately 3.1% IACS compared to copper's 100% IACS, the titanium's superior corrosion resistance and environmental stability often provide better long-term performance in challenging applications. The trade-off in conductivity becomes advantageous when considering total lifecycle costs in corrosive environments.
Q: What welding considerations apply to Grade 2 titanium wire?
A: Grade 2 titanium wire exhibits excellent weldability using TIG welding processes in inert atmosphere environments. Proper shielding prevents contamination that could affect electrical properties, and the material's low heat input requirements minimize distortion while maintaining joint integrity and conductivity across welded connections.
Contact Chuanghui Daye for Premium Grade 2 Titanium Wire Solutions
Ready to enhance your project with reliable Grade 2 titanium wire that delivers exceptional electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance? Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye combines three decades of titanium manufacturing expertise with ISO 9001:2015 certified quality systems to provide customized solutions for your specific requirements. Our Grade 2 titanium wire manufacturer capabilities include various diameters, surface finishes, and mechanical states to match your application needs. Contact our technical team at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your project specifications and receive competitive pricing for volume orders with global shipping support.
References
1. American Society for Testing and Materials. "Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Bars and Billets." ASTM B348-19, West Conshohocken, PA, 2019.
2. Donachie, Matthew J. "Titanium: A Technical Guide, 2nd Edition." ASM International Materials Park, Ohio, 2000.
3. Lutjering, Gerd and James C. Williams. "Titanium: Engineering Materials and Processes." Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2007.
4. Peters, Manfred, Christoph Leyens, Ulrich Schulz, and Wolfgang A. Kaysser. "Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications." Advanced Engineering Materials, Volume 3, Issue 6, 2001.
5. Schutz, R.W. and H.B. Watkins. "Recent Developments in Titanium Alloy Application in the Energy Industry." Materials Science and Engineering A, Volume 243, Issues 1-2, 1998.
6. Zwicker, Ulrich and Helmut Gysler. "Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications." Wiley-VCH Weinheim, Germany, 2005.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email