- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Why Medical Titanium Plate Is Preferred for Surgical Implants?
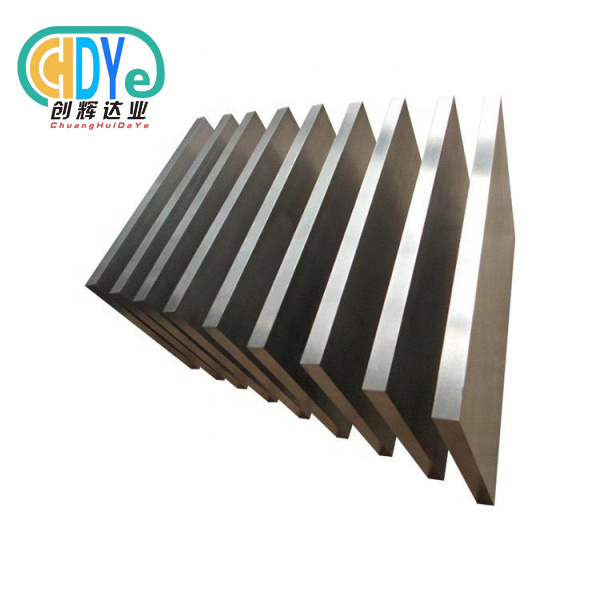
Medical titanium plates are the gold standard for surgical implants due to their biocompatibility, mechanical characteristics, and corrosion resistance. These precision-engineered implant devices provide surgeons and medical device manufacturers with the best bone fixation, cranial reconstruction, and orthopedic solutions. Medical titanium plate materials are essential in modern surgical interventions due to their lightweight, high strength, and tissue compatibility, delivering reliable performance and improved patient outcomes across varied clinical applications.
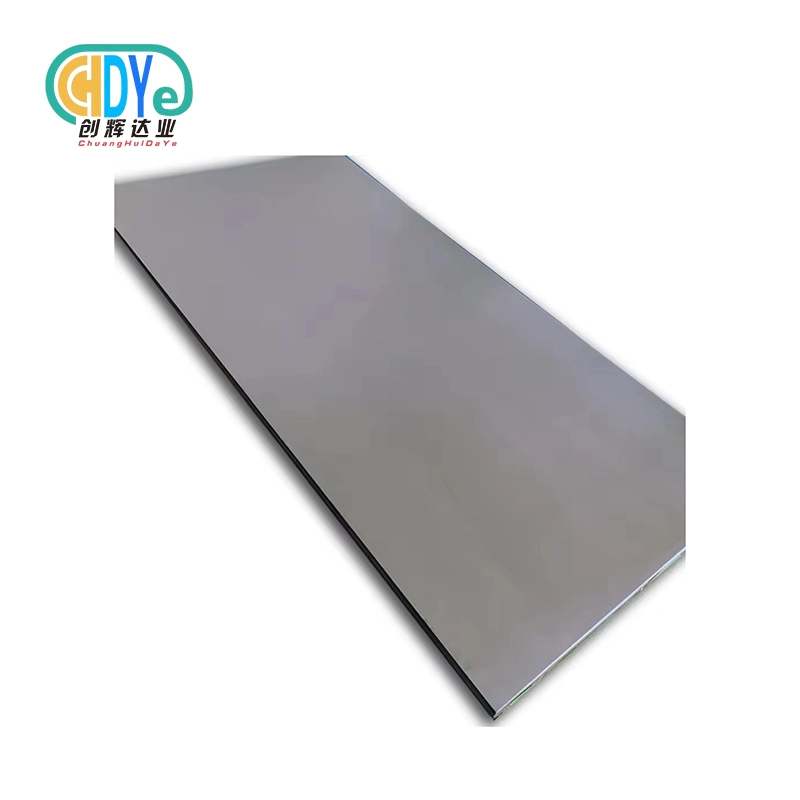
Understanding Medical Titanium Plates: Properties and Benefits
Titanium plates are advanced surgical implants for orthopedic, dental, and reconstructive operations. These precision-made components are made from high-purity titanium and titanium alloys, including Gr 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), Gr 5 ELI (Extra Low Interstitial), and Gr 23 ELI, which have been carefully tested and approved for medical uses.
Fundamental Material Properties
Titanium is ideal for surgical implants due to its unique features. Titanium resists corrosion in physiological situations, maintaining structural integrity under bodily fluids and salty conditions. Non-magnetic substance allows reliable post-surgical monitoring without implant removal by preventing MRI scan interference.
Titanium, with a density of 4.5 g/cm³, is lighter than stainless steel yet still has higher mechanical strength. Our ideal strength-to-weight ratio decreases bone tissue stress and provides structural support during recovery. Stress shielding that can jeopardize implant success is reduced by the material's modulus of elasticity, which matches human bone.
Biocompatibility and Tissue Integration
Titanium forms a persistent oxide layer when exposed to oxygen, preventing metal ion escape into surrounding tissues, making it biocompatible. This eliminates allergic and inflammatory symptoms associated with other metallic implant materials. In clinical tests, titanium implants improve osseointegration, allowing bone tissue to grow directly onto the implant surface without fibrous scar tissue.
Various therapies can modify medical titanium plate surfaces to improve bone-implant integration. Micro-textured surfaces from anodization, sand blasting, and acid etching promote cell adhesion and bone development. Implant stability and surgical healing times are greatly improved by these surface changes.
Clinical Applications and Performance
Titanium forms a persistent oxide layer when exposed to oxygen, preventing metal ion escape into surrounding tissues, making it biocompatible. This eliminates allergic and inflammatory symptoms associated with other metallic implant materials. In clinical tests, titanium implants improve osseointegration, allowing bone tissue to grow directly onto the implant surface without fibrous scar tissue.
Various therapies can modify medical titanium plate surfaces to improve bone-implant integration. Micro-textured surfaces from anodization, sand blasting, and acid etching promote cell adhesion and bone development. Implant stability and surgical healing times are greatly improved by these surface changes.
Why Titanium Plates Outperform Other Materials in Surgical Implants?
Surgical success and patient safety depend on implant material choice. Medical experts and procurement specialists must comprehend titanium plates' benefits over other materials to choose and source implants.
Comparison with Stainless Steel Implants
Surgical applications have historically employed stainless steel because of its availability and mechanical strength. Titanium plates have biocompatibility and corrosion resistance advantages. Stainless steel includes nickel, chromium, and iron, which might trigger allergies in sensitive persons. Stress shielding from stainless steel's higher elastic modulus may cause bone resorption near implant sites.
Titanium's corrosion resistance prevents metal ion release, preventing tissue response and implant degeneration. The material's reduced elastic modulus matches bone characteristics, enabling natural load transmission and decreasing implant loosening. Titanium plates are best for permanent implants that require long-term biocompatibility.
Advantages Over Ceramic Implants
Ceramic materials are biocompatible and attractive, especially in dentistry. However, their brittleness limits its employment in load-bearing applications that require impact resistance. Titanium plates are better for orthopedic applications with high mechanical pressures due to their fracture toughness.
Titanium machinability provides precise implant geometry customization to satisfy patient anatomical needs. Ceramic materials are harder to process and change, restricting design flexibility and raising manufacturing costs. Ductility protects against catastrophic failure because titanium deforms before fracture, signaling implant issues.
Performance Against Biodegradable Alternatives
Polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid implants biodegrade naturally. These materials may degrade at unpredictable rates and lack the mechanical strength needed for load-bearing applications, compromising surgical outcomes.
Titanium plates maintain mechanical qualities over time, ensuring important application reliability. The permanence of titanium implants avoids concerns about premature degradation or structural support loss over long healing periods. Titanium plates are best for high-stress surgeries that require long-term durability although biodegradable variants may work.
Procurement Considerations for Medical Titanium Plates
Understanding regulatory criteria, quality standards, and supplier skills is essential for medical titanium plate procurement. B2B purchasers must consider numerous criteria to comply with medical device standards and source cost-effectively.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Medical titanium plates must meet strict international standards for patient safety and regulatory approval. ASTM F136 covers the popular Ti-6Al-4V alloy, while ASTM F67 governs unalloyed titanium for surgical implants. For medical device clearance, manufacturers must meet certain chemical composition, mechanical property, and testing standards.
Medical device manufacturers with ISO 13485 accreditation use quality management systems intended for this industry. This accreditation guarantees production, quality control, and documentation satisfy international medical device manufacturing standards. Buyers should check that suppliers have current certifications and can offer batch-specific traceability evidence.
FDA or CE marking standards vary by market and application. Procurement specialists must grasp target market regulations to ensure sourced materials meet all standards. Working with vendors with regulatory experience helps speed up product approval and time-to-market.
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Assurance
Manufacturing, quality, and technical skills must be assessed to find dependable suppliers. High-quality titanium plates require extensive melting, forging, and machining skills from established producers. Precision rolling and annealing create medical-grade mechanical qualities, while vacuum melting furnaces maintain purity.
Comprehensive quality control techniques should include chemical composition analysis, mechanical property verification, and surface quality inspection. Ultrasonic and eddy current tests find intrinsic flaws that could affect implant performance. For consistent quality, suppliers should supply complete test certifications and statistical process control data.
When ordering custom titanium plates for specific applications, manufacturing flexibility is essential. For research and development, suppliers with substantial machining skills can make patient-specific implants and prototypes. Rapid prototyping and small-batch production meet medical device and research institution needs.
Cost Analysis and Sourcing Strategies
Competitive product development requires cost-effective titanium material procurement because titanium material prices make up a large part of medical implant manufacturing. Working directly with titanium producers reduces material prices and ensures supply chain reliability. However, purchasers must balance cost, quality, and supplier skills.
Volume purchase agreements reduce costs and guarantee supplies. These arrangements help buyers and sellers predict demand and optimize production planning. When assessing supplier proposals, buyers should consider total cost of ownership, including transportation, inventory, and quality costs.
Geographic factors affect cost and lead time. Titanium-producing suppliers may have lower shipping costs and established supply chains. When choosing overseas providers, buyers must additionally consider technical support, communication efficiency, and time zone compatibility.
How Medical Titanium Plates Work in Surgical Implantation and Healing?
Medical device developers and procurement experts benefit from understanding how medical titanium plates work in surgery. This knowledge aids product specification, quality, and performance decisions.
Mechanical Function and Load Transfer
Titanium plates keep bones aligned during fracture and surgery healing. These devices distribute mechanical pressures across bone surfaces to prevent fragment displacement during natural healing. Plate geometry and attachment method determine fixation system stability and load transfer.
Titanium's elastic modulus matches cortical bone, distributing stress more physiologically than stiffer materials. Mechanical compatibility reduces stress shielding and implant-site bone resorption. The implant and surrounding bone tissue should share load to remodel bone and maintain fixation stability.
Screw attachments hold titanium plates to bone tissue and provide controlled healing mobility. Locking screw designs generate fixed-angle structures that stabilize osteoporotic bone or complex fracture patterns. Plate stiffness and screw configuration can be customized for clinical applications and patient situations.
Biological Integration and Osseointegration
Implant success depends on complex cellular processes that respond to titanium implants. Titanium surfaces interact with blood proteins and cells after implantation, starting a healing cascade. The stable oxide layer on titanium surfaces encourages protein adsorption and cell growth.
Titanium surfaces stimulate bone-forming osteoblast cells more than other metallic materials. Collagen and other proteins from these cells build the organic matrix for growing bone. Long-term stability is better than fibrous encapsulation with other implant materials because osseointegration directly contacts bone tissue and titanium surfaces.
Topography and chemistry can improve titanium implant biological response. Sandblasting or acid etching creates micro-textured surfaces that increase surface area and mechanically retain cells. These changes speed up implant healing and improve stability in clinical settings.
Healing Timeline and Long-term Performance
Following titanium plate implantation, different biological and mechanical processes occur during healing. The first week of inflammation comprises blood clot formation, cellular infiltration, and tissue healing. The titanium plate provides instant mechanical support while biological mending mechanisms begin.
New blood vessels and cellular growth occur during the repair phase, which lasts a week to many months. Osteoblast activity peaks during this time, forming significant bone around the implant. While gradually shifting loads to healing bone tissue, the titanium plate provides structural support.
Reorganizing freshly created bone tissue to enhance strength and function can take months to years. Long-term tests show that correctly integrated titanium implants can last decades without degrading. Medical personnel can monitor healing progress and spot issues early with radiographic imaging.
Trusted Brands and Supplier Overview
Several implant development and production-proven firms sell medical titanium plates. Understanding supplier strengths and capabilities helps procurement experts source products with quality and regulatory compliance.
Global Market Leaders
DePuy Synthes, Stryker, and Zimmer Biomet dominate the titanium implant market with substantial research and development. These firms have extensive product portfolios for surgical specialties and applications. Their global distribution networks ensure reliable product and technical assistance worldwide.
In trauma and orthopedic applications, DePuy Synthes offers revolutionary titanium plate designs for challenging surgeries. For optimal performance and patient safety, their products undergo rigorous testing and clinical validation. Implant design and production are advanced by the company's R&D.
Strategic acquisitions and inventive product development help Stryker advance surgical technologies. Their titanium implants are spine, trauma, and craniomaxillofacial-specific. Surgeon education and training help the company improve clinical results and market uptake of innovative technology.
Specialized Suppliers and Custom Manufacturers
DePuy Synthes, Stryker, and Zimmer Biomet dominate the titanium implant market with substantial research and development. These firms have extensive product portfolios for surgical specialties and applications. Their global distribution networks ensure reliable product and technical assistance worldwide.
In trauma and orthopedic applications, DePuy Synthes offers revolutionary titanium plate designs for challenging surgeries. For optimal performance and patient safety, their products undergo rigorous testing and clinical validation. Implant design and production are advanced by the company's R&D.
Strategic acquisitions and inventive product development help Stryker advance surgical technologies. Their titanium implants are spine, trauma, and craniomaxillofacial-specific. Surgeon education and training help the company improve clinical results and market uptake of innovative technology.
Supplier Selection Criteria
Potential suppliers must be evaluated for technical competence, quality systems, and business practices. The items and specifications providers may deliver depend on manufacturing equipment and process capabilities. Advanced melting and processing equipment assures medical-grade material purity and consistency.
Suppliers with quality management systems certification guarantee product quality and regulatory compliance. ISO 13485 certification ensures medical device quality and supplier capability. Supplier facilities are audited regularly to ensure quality and identify improvement opportunities.
When creating new goods or meeting application needs, technical support is essential. Engineering-trained suppliers can advise on material selection, design optimization, and production viability. Collaboration helps product development succeed and avoid costly design changes late in the process.
Conclusion
Biocompatibility, mechanical performance, and long-term reliability make medical titanium plates the chosen surgical implant. The unique mix of lightweight construction, high strength, and tissue compatibility meets modern surgical standards and optimizes patient outcomes. Titanium plates lead implant innovation due to significant clinical data and proven production capability. Medical professionals may trust titanium implant technology for important surgical applications due to careful supplier selection and strict quality criteria.
FAQ
Q: How long does it take for titanium plates to integrate with bone tissue?
A: Titanium plate integration with bone tissue typically occurs over a period of 3 to 6 months, depending on various factors including patient age, overall health, and the specific surgical site. The initial bone healing response begins within days of implantation, but complete osseointegration requires several months of active bone remodeling. Younger patients generally experience faster integration due to higher metabolic activity and bone turnover rates.
The integration process can be monitored through regular radiographic examinations that reveal bone density changes around the implant site. Successful integration is characterized by increased bone density in contact with the titanium surface and the absence of radiolucent lines that might indicate implant loosening or infection.
Q: What certifications are required for medical titanium plates?
A: Medical titanium plates must comply with specific standards and certifications depending on their intended use and target markets. ASTM F67 and ASTM F136 standards govern the material properties and testing requirements for medical-grade titanium and titanium alloys. ISO 13485 certification demonstrates that manufacturers maintain quality management systems appropriate for medical device production.
Regulatory approvals such as FDA 510(k) clearance in the United States or CE marking in Europe are required for commercial distribution of medical titanium plates. These approvals involve a comprehensive review of product design, manufacturing processes, and clinical data to ensure patient safety and product effectiveness.
Q: Are titanium plates safe for long-term implantation?
A: Medical titanium plates have demonstrated excellent long-term safety profiles in clinical applications spanning several decades. The biocompatible nature of titanium prevents adverse tissue reactions, and the material's corrosion resistance ensures stable performance in physiological environments. Long-term studies show success rates exceeding 95% for properly selected and implanted titanium devices.
The safety of titanium implants is further supported by their non-toxic properties and minimal metal ion release. Unlike some other metallic implant materials, titanium does not contain elements known to cause allergic reactions or systemic toxicity. Regular monitoring through clinical examinations and imaging studies helps ensure continued implant safety and function.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Premium Medical Titanium Plates
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye stands ready to support your medical titanium plate requirements with over 30 years of specialized experience in rare metal processing. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing facility in China's Titanium Capital produces high-quality plates compliant with ASTM F67 and ASTM F136 standards. Whether you need Gr 5, Gr 5 ELI, or Gr 23 ELI materials for medical device manufacturing, our advanced melting and machining capabilities deliver precise specifications with full traceability documentation. Contact our technical team at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your medical titanium plate supplier requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your surgical implant projects.
References
1. Geetha, M., Singh, A. K., Asokamani, R., & Gogia, A. K. (2009). Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review. Progress in Materials Science, 54(3), 397-425.
2. Niinomi, M. (2008). Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 1(1), 30-42.
3. Liu, X., Chu, P. K., & Ding, C. (2004). Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 47(3-4), 49-121.
4. Rack, H. J., & Qazi, J. I. (2006). Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 26(8), 1269-1277.
5. Brunette, D. M., Tengvall, P., Textor, M., & Thomsen, P. (2001). Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
6. Williams, D. F. (2008). On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials, 29(20), 2941-2953.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email