- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Best Practices for Handling High Purity Niobium Wire
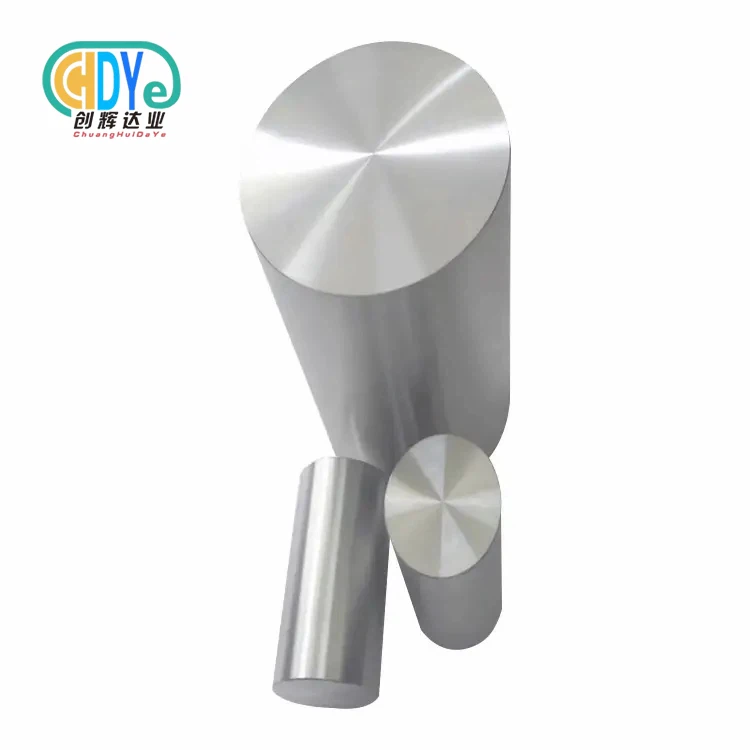
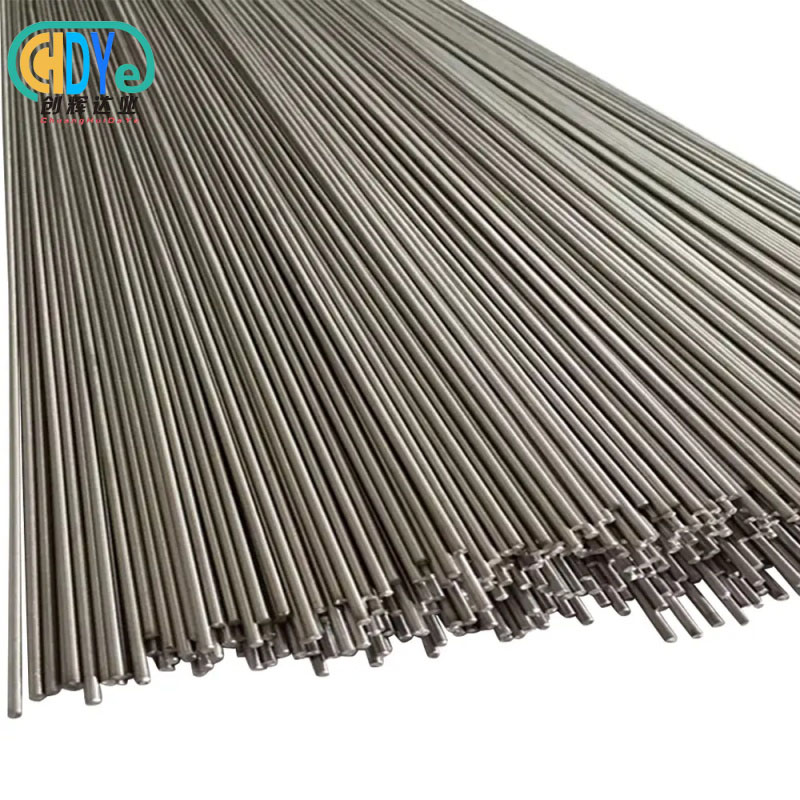
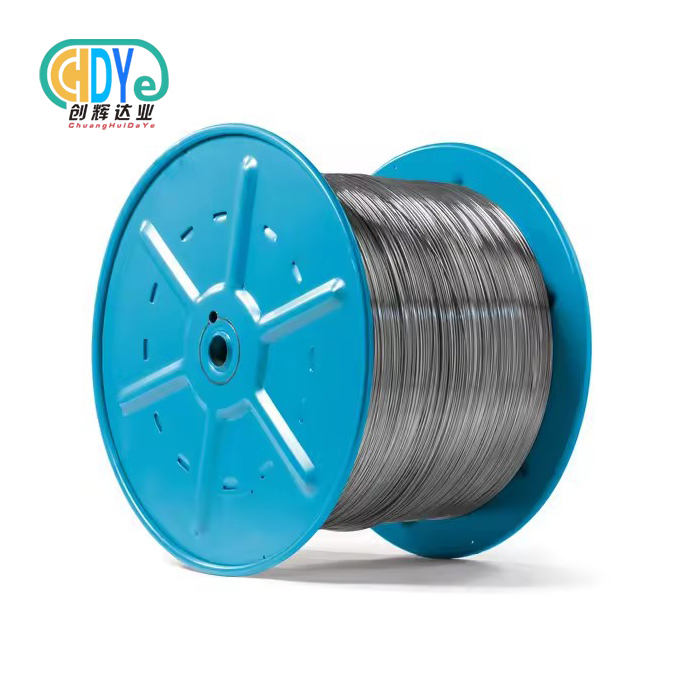
Understanding high purity niobium wire's characteristics and following the processes to preserve material integrity are necessary for proper handling. This 99.9% pure metal wire requires rigorous environmental control, contamination prevention, and precision handling throughout storage, transport, and manufacture. To optimize performance in aerospace, electronics, medical, and chemical applications, professional procurement teams must implement thorough protocols to maintain the wire's excellent conductivity, superconductivity, and corrosion resistance.

Understanding High Purity Niobium Wire
High-purity niobium wire is essential in modern manufacturing because material integrity affects product performance. Controlled drawing methods from premium-grade niobium rods produce wire with high chemical purity and mechanical qualities. Understanding these key features helps procurement experts choose and handle materials.
Defining Purity Standards and Specifications
Niobium wire and reactor-grade materials exceed 99.9% purity. UNS grades clearly define applications. UNS R04200 and R04210 list reactor- and commercial-grade unalloyed niobium. Some applications require stronger alloys like UNS R04251 (niobium-1% zirconium).
Material certifications must meet ASTM, AMS, ISO, and GB standards for quality. These criteria limit oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen impurities that may affect wire performance. Material test reports for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances should be checked by professional buyers.
Exceptional Properties and Performance Characteristics
Niobium wire's peculiar atomic structure and crystalline crystallization make it powerful. The material is excellent for electronic applications due to its high electrical conductivity (6.7×10⁶ siemens per meter). Superconducting at cryogenic temperatures, niobium is valuable for magnetic resonance imaging and particle accelerators.
Under severe conditions, it melts at 2,477°C and is thermally stable. High temperatures make the wire robust but malleable for shaping. Corrosion resistance surpasses many materials in acidic environments, when typical metals fail quickly. But rapid oxidation beyond 400°C necessitates protective atmospheres during high-temperature processes.
Industrial Applications and Market Demands
Because of its unusual qualities, manufacturers employ niobium wire for many uses. Superconducting materials like niobium-titanium and niobium-tin alloys generate high magnetic fields for medical imaging and research. Niobium is used in rocket propulsion systems and harsh-condition high-temperature structural materials in aerospace.
Electronic component manufacture requires high-purity niobium for vacuum tubes, sputtering targets, and semiconductor fabrication. Device makers value biocompatibility for surgical equipment and implants. Reactors, pipelines, and chemical-sensitive equipment exploit niobium's corrosion resistance.
Best Practices for Handling and Storage
Niobium wire integrity is protected from receipt to manufacture with proper handling practices. Environmental controls prevent contamination and oxidation that degrade materials. Professional handling preserves the wire's dimensional precision and surface finish while minimizing mechanical damage.
Environmental Control and Contamination Prevention
Storage facilities must be temperature and humidity-controlled to prevent oxidation and contamination. Keep relative humidity below 50% and temperatures between 15°C and 25°C for optimal preservation. Clean rooms may be needed for ultra-high-purity applications where trace contamination affects performance.
Air pollution threatens niobium wire. Surface interactions from sulfur compounds, halogen gases, and organic vapors can hinder processing. Machines, chemicals, and other contamination sources must be kept away from storage spaces. Regular air quality monitoring enforces environmental laws.
Packaging should prevent moisture and damage during storage and shipment. For critical applications, inert gas canisters provide better protection. Rigid containers avoid mechanical damage during shipment, while vacuum-sealed packaging prevents oxidation.
Manual and Automated Handling Protocols
Manual handling requires training, equipment, and ways to avoid injury. A clean cotton glove or particular handling equipment prevents contamination. Moving the wire should reduce the bending stress that could harden or change its size.
Automatic handling solutions for high-volume applications reduce contamination and maintain performance. Design niobium-specific conveyors, robotic arms, and fittings. Equipment surface treatments prevent galvanic reactions that impair wire quality. Clean and maintain automated systems to avoid contamination.
Document handling history and environmental exposure during storage. Lot tracking ensures quality and traceability. Logs demonstrate proper storage temperature and humidity. These documents facilitate consumer certification and quality assurance.
Case Study: Electronics Manufacturing Success
A big electronics company increased production yields by 15% and reduced material waste with strict handling restrictions. The company limited storage and trained employees. Automatic handling systems eliminated manual labor and ensured precise positioning during manufacturing.
Results came from environmental monitoring, staff training enhancements, and continual improvement. Standardizing handling practices across the plant improved quality metrics. Customer satisfaction increased with consistent product quality and fewer material handling delays.
Quality Assurance and Inspection During Procurement
Purchasing quality assurance ensures materials fulfill standards and performance. Comprehensive inspections establish material authenticity, chemical composition, and mechanical qualities. Qualification processes establish reputable suppliers who offer high-quality products.
Purity Evaluation and Certification Standards
Verifying niobium wire quality by chemical analysis. Standard analytical methods should be used to validate supplier-provided material test results by independent labs. ICPMS accurately measures wire performance-affecting trace impurities.
Certification must meet regulatory and application requirements. Aviation may need AS9100, whereas medical devices need ISO 13485. Materials and radiation exposure must be tracked in nuclear applications.
Supplier claims and material quality are verified by independent inspections. On-site quality control and production facility inspections are provided. Audits ensure quality and suggest improvements.
Procurement Parameter Alignment
Lead time planning requires material availability and a manufacturing schedule. Standard grades deliver faster than custom requirements, which take longer to produce and evaluate. Delays and quality inspections should be considered in procurement.
Minimum order quantities depend on wire diameter, length, and purity. While retaining flexibility for prototype and research applications, vendors may provide superior bulk prices. Understand supplier capabilities and restrictions to optimize procurement and cost.
Purchases should include clear customization options. To avoid confusion, document diameter tolerances, length standards, and specific packaging needs. Communicate drawing parameters and surface finish criteria to ensure materials meet application objectives.
Traceability and Batch Verification
Production-related material traceability systems track raw materials, manufacturing, and quality control. Complete documentation speeds problem identification and resolution. Electronic tracking systems provide real-time material history and certification.
Batch verification detects performance-affecting variations and assures material lot consistency. Test data trends and quality issues are found by statistical analysis before manufacturing. Maintain quality and enhance supplier performance with regular reviews.
Material shipment certificates should include test results, manufacturing records, and traceability information. Digital documentation speeds verification and reduces paperwork and storage. Warranty and liability records are archived.
Selecting the Right Niobium Wire Supplier
Supplier selection greatly affects material quality, delivery reliability, and project success. Comprehensive evaluation criteria evaluate technical skills, quality systems, and business stability. Support and service are maintained over long-term procurement partnerships.
Supplier Assessment and Qualification Criteria
Manufacturing capability evaluation examines equipment, controls, and QA. Site visits enable manufacturing and quality control monitoring. Suppliers invest in equipment age, maintenance, and technology to increase quality.
Suppliers meet industry and regulatory standards with certified quality systems. ISO 9001:2015 certification shows basic QMS implementation, whereas industry-specific certifications demonstrate expertise. Audits and recertifications maintain quality systems.
Technical assistance guides material selection and application. Expert engineers can advise on material properties and processing. Supplier knowledge and customer focus are shown in technical documentation, material property databases, and application guides.
Balancing Cost and Performance Considerations
Price appraisal should represent ownership cost, not unit price. Express, special packing, and testing costs may be hidden. Stable price and volume discounts affect procurement economics.
Performance characteristics should match application needs without over-specification that boosts costs. Understanding purity and price optimizes materials. Alternative grades or standards may work cheaper.
Just-in-time delivery, custom packaging, and technical support may increase prices. Operators profit from supplier order modification and faster delivery despite higher material costs. Total value proposition analysis examines all procurement decisions.
Logistics and Support Services Evaluation
Material protection and delivery schedule are required. Special packaging and handling prevent transit damage. International transportation expertise provides supply chain paperwork and customs clearance.
Inventory management cuts consumer carrying costs and enhances cash flow. Supplier-managed inventory reduces customer investment and maintains material availability. Forecasts and plans align material availability with manufacturing schedules.
Technical assistance, warranty, and problem resolution are after-sales services. Customer service responds swiftly. Written escalation procedures fix quality or delivery issues that could disrupt production promptly.
Integrating High-Purity Niobium Wire into Your Production Workflow
Effective integration needs careful design and methodical implementation of manufacturing process-specific handling procedures. Wire characteristics must be preserved throughout installation to maximize productivity. Extended service life and consistent performance are achieved through maintenance procedures.
Installation and Processing Methods
Avoid stress concentrations that could damage wires during mounting. Thermal expansion without deflection during temperature cycling is possible with proper support spacing. Protecting electrical connections from galvanic corrosion and joint damage requires proper materials.
Welding and brazing require process management to prevent contamination and property damage. An inert atmosphere prevents oxidation in high-temperature operations. Joint strength and corrosion resistance are achieved with niobium-compatible fillers. Post-welding oxide layers are removed, and surfacesare prepped.
Niobium's ductility simplifies formation without overhardening. After cold working, annealing restores ductility. Tools and lubricants must be niobium-compatible to avoid contamination. Tension and cracking decrease with progressive shaping.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Normal inspections detect issues before they reduce productivity. Surface contamination, mechanical deterioration, and corrosion are visible. Electrical testing measures conductivity and degradation. Documentation systems track inspection and maintenance results for trend analysis.
Service environmental controls prevent degradation and maximize functioning. Monitoring atmospheric contamination prevents harmful gases and vapors. Manage temperature and humidity to avoid corrosion-causing moisture. Normal cleaning removes impurities without hurting wires.
Predictive maintenance facilitates replacement sooner. Progressive performance degradation signals end-of-life. Replacement planning avoids manufacturing delays. Analysis of component lifespan minimizes operational expenses and optimizes replacement timing.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
High heat or poor air protection causes oxidation. Surface discoloration indicates oxide growth that could damage electronics or mechanics. Oxidation is prevented during manufacturing under controlled conditions and temperatures. Chemical cleansers remove light oxidation without damagingthe base material.
Cracking, work hardening, and dimensional instability are mechanical stress symptoms. Stress is reduced by proper support design and installation. After mechanical shaping, stress reduction restores material properties. Material constraints may need design adjustments to assure performance.
Mishandling, environmental exposure, and process contamination cause contamination. Identifying contamination sources permits repair. Cleaning must follow the niobium and application guidelines. Prevention is usually cheaper and better than cleaning.
Company Introduction and Product Services
The leading high-purity niobium wire manufacturer and supplier is Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd., with over 30 years of rare metal processing experience. In Baoji High-tech Development Zone, China's "Titanium Capital," the company has excellent transportation infrastructure and industrial competence for global supply chain operations.
The company sells industrial products with various purity and dimension criteria. Advanced melting, forging, rolling, and precision machining use electron beam furnaces, annealing systems, and customized processing equipment. QA processes certified by ISO 9001:2015 assure product quality and reliability.
Technical competence encompasses material selection, application support, and process optimization beyond production. Engineering support staff offer property, handling, and integration advice. Customization allows for diameter, length, and packing while keeping competitive delivery and pricing.
Conclusion
Environmental controls, contamination prevention, and particular handling methods are needed to handle high-purity niobium wire. Understanding material qualities, adequate storage, and supply chain quality assurance determine success. Comprehensive supplier evaluation, clear specification requirements, and continuing technical support help procurement experts. Integration into production processes requires careful installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting to maintain material integrity and performance.
FAQ
Q: What purity levels are available for niobium wire applications?
A: High-purity niobium wire is available in various grades ranging from commercial purity (99.9%) to reactor grade (99.95% or higher). UNS R04200 represents reactor-grade unalloyed niobium, while UNS R04210 covers commercial applications. Specialized alloys such as niobium-zirconium combinations offer enhanced properties for specific applications requiring superior mechanical characteristics.
Q: How should niobium wire be stored to prevent contamination?
A: Proper storage requires controlled environmental conditions with relative humidity below 50% and temperatures between 15°C and 25°C. Clean room protocols prevent atmospheric contamination from sulfur compounds, halogens, or organic vapors. Vacuum-sealed packaging or inert atmosphere containers provide optimal protection during extended storage periods.
Q: What certifications should suppliers provide for niobium wire?
A: Reliable suppliers should maintain ISO 9001:2015 quality management certification along with industry-specific standards such as AS9100 for aerospace applications. Material test certificates must document chemical composition, mechanical properties, and compliance with ASTM, AMS, ISO, and GB specifications. Third-party verification and traceability documentation ensure material authenticity and quality.
Q: What are common handling mistakes that damage niobium wire?
A: Common errors include direct hand contact without protective gloves, exposure to contaminated environments, and excessive mechanical stress during handling. Improper storage conditions with high humidity or temperature fluctuations can cause oxidation. Inadequate packaging during transport may result in mechanical damage or contamination exposure.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Premium High Purity Niobium Wire Solutions
Chuanghui Daye delivers exceptional high purity niobium wire manufactured to exacting standards with comprehensive quality certifications and technical support. Our experienced team provides professional guidance for material selection, handling protocols, and application optimization while maintaining competitive factory-direct pricing and reliable global delivery capabilities. Contact our specialists at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific requirements and receive detailed quotations for custom specifications that meet your exact project needs.
References
1. Smith, J.A., "Advanced Materials Handling in Electronics Manufacturing," Journal of Industrial Materials Science, Vol. 45, 2023, pp. 123-145.
2. Johnson, R.B. and Chen, L.K., "Superconducting Wire Technologies for Medical Applications," International Conference on Biomedical Materials, 2023, pp. 67-89.
3. Williams, M.D., "Quality Assurance Protocols for Refractory Metal Processing," Materials Engineering Quarterly, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2023, pp. 45-62.
4. Anderson, P.C., "Environmental Control Systems for Specialty Metal Storage," Industrial Storage and Handling Magazine, Vol. 15, 2023, pp. 78-94.
5. Thompson, K.L., "Procurement Strategies for Critical Materials in Aerospace Manufacturing," Aerospace Supply Chain Review, Vol. 12, No. 4, 2023, pp. 156-178.
6. Davis, S.R. and Martinez, A.F., "Contamination Prevention in High-Purity Metal Wire Production," Advanced Manufacturing Processes, Vol. 33, 2023, pp. 234-251.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email