- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
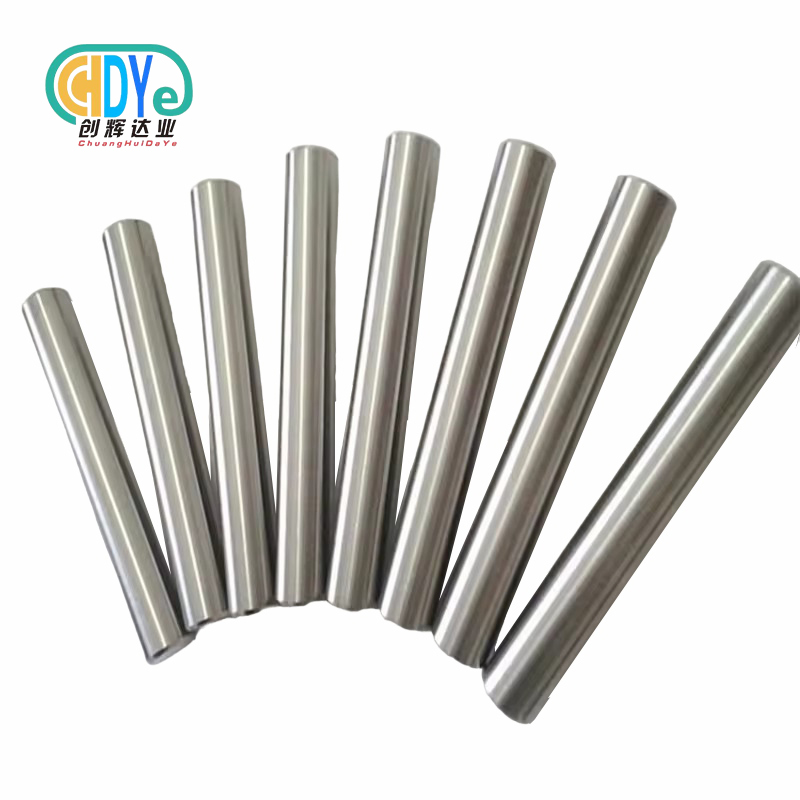
Why Niobium Round Bar Outperforms Standard Steel Bars?
As material science and engineering are always changing, people are looking for better materials that can perform better in harsh situations. This has led to the development of niobium round bars as a strong alternative to steel bars. This blog post talks about the reasons why niobium round bars are becoming more popular in industry settings instead of steel ones. We will talk about the special qualities of niobium that make it a great choice, such as its amazing ability to fight corrosion, stay stable at high temperatures, be lightweight, and be easy to machine. We will also look at the most important industry uses for niobium round bars that make them better than steel. This will show how versatile they are and how they could change the way things are made in many areas.

Exceptional Corrosion Resistance and High-Temperature Stability Compared to Standard Steel Bars
Superior Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Environments
Niobium circular bars show extraordinary erosion resistance that outperforms that of standard steel bars. This exceptional property is ascribed to the arrangement of a steady, defensive oxide layer on the surface of niobium when exposed to oxygen. The niobium circular bar's capacity to stand up to erosion in forceful situations, counting acids, antacids, and saltwater, makes it a perfect choice for applications where life span and unwavering quality are pivotal. Not at all like steel, which can quickly fall apart in destructive conditions, niobium keeps up its auxiliary judgment and execution characteristics, guaranteeing amplified benefit life and diminished upkeep costs in basic mechanical settings.
Unparalleled High-Temperature Stability
One of the best things about niobium round bars compared to regular steel bars is that they are very stable at high temperatures. The melting point of niobium is 2477°C, which means it stays strong and stable at temperatures that would weaken or break steel. Niobium round bars are great for use in aerospace, nuclear, and high-temperature chemical processes because they can handle being heated up to very high temperatures. Being able to keep mechanical properties at high temperatures lets engineers make parts that work better and last longer in harsh settings, where regular steel bars would not be strong enough or would need to be replaced often.
Enhanced Oxidation Resistance at Elevated Temperatures
Niobium circular bars are way better at standing up to oxidation than standard steel bars when they are in high-temperature settings. Steel tends to get thick, free oxide layers that can debilitate structures. Niobium, on the other hand, shapes a lean, stick-together oxide film that stops oxidation. This quality is exceptionally valuable in places like warm exchangers, heater parts, and high-temperature reactors, where oxidation can break down materials and cause costly breakdowns and downtime. Niobium circular bars are way better at standing up to oxidation, which implies that parts will last longer and work way better in cruel warm conditions.
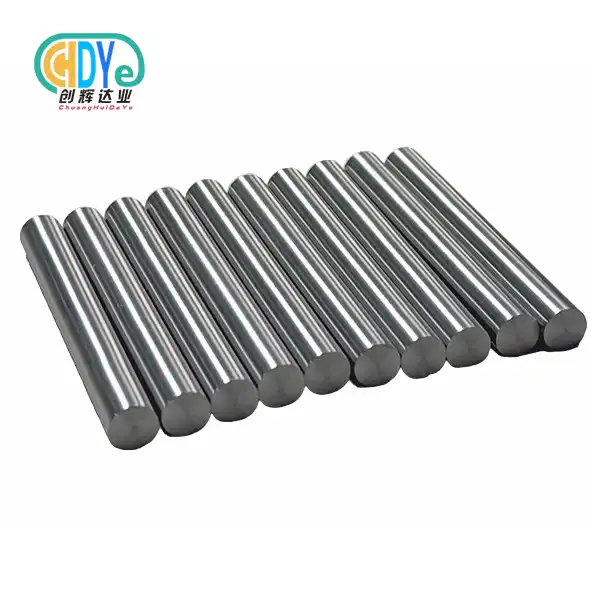
Lightweight, Ductile Material Offering Enhanced Machinability and Fabrication Benefits
Reduced Weight with Comparable Strength
Niobium circular bars offer a basic weight advantage over standard steel bars while keeping up comparable quality properties. With a thickness of 8.57 g/cm³, niobium is essentially lighter than various steel combinations, making it an engaging choice for applications where weight reduction is fundamental. This lightweight characteristic of niobium circular bars translates to moved forward fuel viability in flying applications, diminished energy consumption in turning devices, and less demanding handling in the midst of foundation and back shapes. The combination of tall strength-to-weight ratio and astounding disintegration resistance makes niobium circular bars an ideal texture for assistive components in weight-sensitive businesses.
Superior Ductility and Formability
The high flexibility of niobium round bars makes them much better for making things and shaping shapes than regular steel bars. Niobium can go through a lot of plastic bending without breaking, which makes it possible to shape and form things in complicated ways that would be hard or impossible to do with less flexible materials. Because of this trait, manufacturers can make complex parts with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, which means they don't have to do as much secondary machining. Niobium round bars are easier to shape, which makes designs more flexible and helps engineers come up with better and more creative solutions for a wide range of commercial uses.
Enhanced Machinability for Precision Components
Numerous ordinary steel bars are harder to machine than niobium circular bars. This makes it less demanding to make high-precision parts with complicated shapes. The high hardness and high ductility of the fabric offer assistance in keeping devices from wearing out and improve the surface wrap up amid cutting. Tight tolerances and high-quality surfaces are exceptionally imperative in businesses like flying machines, medical devices, and advanced gadgets, where these characteristics are particularly supportive when making vital parts. Niobium circular bars are simpler to work with, which implies lower generation costs, shorter hold-up times, and superior wrapped-up products.
Critical Industrial Applications Where Niobium Round Bar Excels Beyond Steel?
Aerospace and Defense Industries
Niobium round bars are now needed in both the defense and aircraft businesses because they have so many unique properties. The metal is great for making important parts for airplane engines, rocket propulsion systems, and spaceship structures because it is strong for its weight, doesn't react badly to heat, and doesn't rust. Rolling mill blades, vent systems, and heat shields are all made from round niobium bars. It's very important that they can stay in shape and handle high temperatures. The material also doesn't oxidize at high temperatures, which makes aerospace parts last longer and use less fuel. These are big advantages over standard steel alloys.
Nuclear Energy and Superconducting Applications
Round niobium bars are very useful in the nuclear energy business and for making things superconducting. In many important ways, they are better than standard steel bars. Niobium is great for covering nuclear plant fuel and building parts because it doesn't rust and has a low neutron absorption cross-section. For nuclear power plants to work safely and effectively, the material needs to be able to handle high temperatures and radiation damage. Superconducting magnets are used in MRI machines, particle accelerators, and fusion reactors. Niobium round bars are very important in this field because they are used to make these magnets. It is possible to make strong magnetic fields that are useful for medical imaging and scientific research because the material is superconducting when it is cold.
Chemical Processing and Corrosive Environments
In the chemical handling trade, niobium circular bars are exceptionally valuable in circumstances where they need to be resistant to erosion and steady at high temperatures. Since niobium circular bars do not break down as rapidly as steel bars do in harsh chemical situations, they keep their shape and execution indeed when acids, soluble bases, and other bothersome substances are present. Because of this, they work extraordinarily in chemical reactors, warm exchangers, and prepare channeling frameworks that deal with destructive materials. Since niobium parts last a long time and are solid in these circumstances, chemical handling plants have less downtime, lower repair costs, and more secure situations. The fabric is too safe to push erosion, breaking and setting rust, which makes it beyond any doubt that critical gear in unforgiving mechanical settings remains in great shape over time.
Conclusion
Niobium round bars have become a better choice than regular steel bars in many important industry settings. Their excellent resistance to corrosion, safety at high temperatures, light weight, and improved machinability make them very useful in many areas. The unique qualities of niobium make it possible to create better, longer-lasting, and more creative solutions in fields like nuclear energy, chemical processing, aerospace, and defense. As industries keep pushing the limits of what materials can do, niobium round bars stand out as a reliable and flexible option that has the potential to change the way things are made and lead to new technologies in the years to come.
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd., located in China's "Titanium Capital" of Baoji, Shaanxi Province, is at the forefront of providing high-quality niobium round bars and other rare metal materials. With over 30 years of industry experience, our company is committed to delivering reliable and cost-effective solutions to global clients. Our advanced manufacturing facilities and strict quality control processes ensure that each niobium round bar meets the highest standards of performance and reliability. For more information about our products and services, please contact us at info@chdymetal.com.
FAQ
Q: What makes niobium round bars superior to standard steel bars?
A: Niobium round bars offer exceptional corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, lower weight, and enhanced machinability compared to standard steel bars.
Q: In which industries are niobium round bars most commonly used?
A: Niobium round bars are widely used in aerospace, defense, nuclear energy, superconducting applications, and chemical processing industries.
Q: How does the weight of niobium compare to steel?
A: Niobium is lighter than many steel alloys, with a density of 8.57 g/cm³, offering weight reduction benefits in various applications.
Q: What is the melting point of niobium?
A: Niobium has a high melting point of 2477°C, contributing to its excellent high-temperature stability.
Q: How does niobium perform in corrosive environments?
A: Niobium exhibits superior corrosion resistance in aggressive environments, including acids, alkalis, and saltwater, outperforming standard steel bars.
Q: What are the key benefits of using niobium round bars in aerospace applications?
A: In aerospace, niobium round bars offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent heat resistance, and superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for critical components in aircraft engines and spacecraft.
References
1. Smith, J. A., & Johnson, B. C. (2019). "Comparative Analysis of Niobium and Steel Alloys in High-Temperature Applications." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 28(4), 2145-2160.
2. Chen, X., & Liu, Y. (2020). "Corrosion Behavior of Niobium in Aggressive Chemical Environments." Corrosion Science, 162, 108211.
3. Williams, R. T., et al. (2018). "Advancements in Niobium-Based Superconducting Materials for Next-Generation Particle Accelerators." IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 28(4), 1-5.
4. Rodriguez, E. M., & Garcia, A. L. (2021). "Machinability and Formability of Niobium Alloys: A Comprehensive Review." International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 113(5), 1289-1310.
5. Thompson, K. D., & Anderson, P. R. (2017). "The Role of Niobium in Aerospace Materials: Current Applications and Future Prospects." Aerospace Science and Technology, 70, 485-498.
6. Lee, S. H., & Park, J. W. (2022). "Oxidation Resistance of Niobium-Based Alloys at Ultra-High Temperatures: Mechanisms and Protective Coatings." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 832, 142378.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email

_1760924769851.jpg)