The chemical processing industries are constantly confronted with issues relating to the corrosion of equipment, the deterioration of materials, and the effectiveness of their operations. The ASTM B 265 titanium sheet provides outstanding corrosion resistance, an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, and dependable performance in situations that are characterized by extreme chemical conditions. These titanium alloy sheets offer long-term durability while simultaneously lowering the expenses of maintenance and the amount of time spent offline. Because the defined standards guarantee that all grades have the same quality and mechanical properties, they are an excellent choice for pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and chemical tanks, all of which are applications in which the integrity of the material is of the utmost importance.
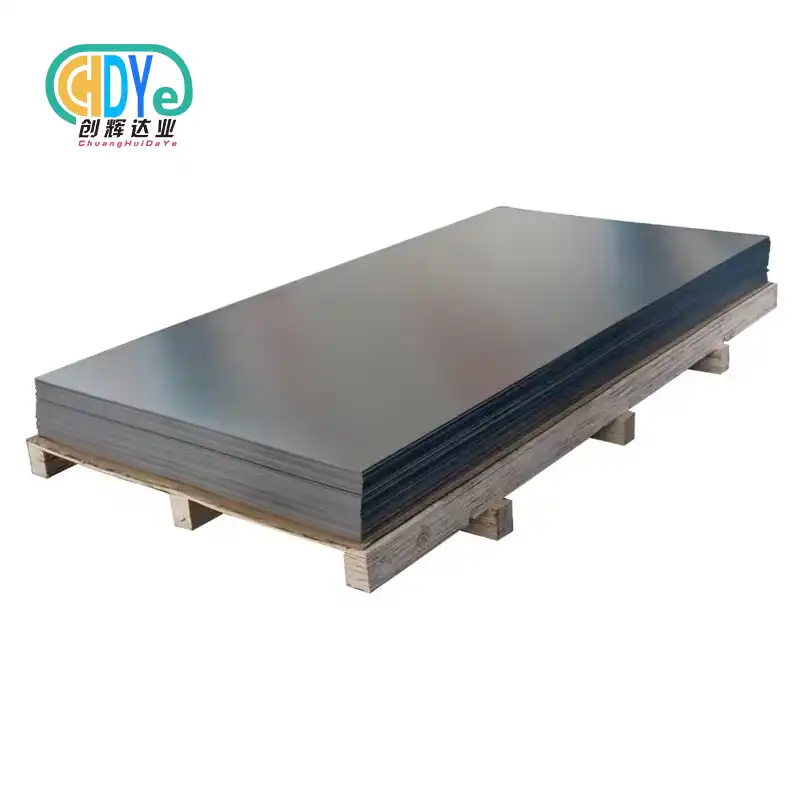
Key Performance Parameters of ASTM B 265 Titanium Sheet
The engineers are able to select the appropriate grade for certain chemical processing applications when they have a thorough understanding of the technical parameters. A number of grades are included in the standard, each of which has a unique set of features that are intended to meet a certain set of operational needs.
Titanium sheet of grade 2 is the pure grade that is utilized in commercial applications the most frequently. The tensile strength ranges from 40 to 65 ksi, while the yield strength ranges from 25 to 40 ksi. It offers exceptional resistance to corrosion. Because the elongation reaches a minimum of twenty percent, it offers excellent formability for intricate shapes.
The presence of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium in grade 5 titanium sheet results in the formation of an alloy with high strength. The yield strength is between 120 and 135 ksi, while the tensile strength falls somewhere between 130 and 145 ksi. This particular grade possesses high mechanical qualities while also preserving an excellent resistance to chemical substances.
The thickness of titanium sheets can range anywhere from 0.020 inches to 4.000 inches, making it suitable for a wide range of manufacturing applications. A smooth, consistent texture that is suited for welding and forming processes is present in the surface finish, which satisfies the norms of the industrial sector.
The chemical composition adheres to the ASTM requirements in a stringent manner. The titanium percentage of pure titanium grades ranges from 99.2% to 99.5%, with the levels of oxygen, nitrogen, and iron being carefully controlled. The compositions of titanium alloys comprise specific amounts of aluminum, vanadium, and other alloying elements with the purpose of improving their qualities.
Core Benefits for Chemical Processing Applications
Materials that are able to survive challenging environments while preserving their structural integrity are in high demand in the chemical industry. When exposed to these difficult conditions, the corrosion resistance of titanium sheet is superior to that of the majority of conventional metals.
Because of their excellent resistance to chloride conditions, these sheets are extremely useful for applications involving seawater and facilities that produce chlorine. Titanium, in contrast to stainless steel, is able to keep its protective oxide layer intact even when exposed to highly corrosive solutions that contain hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and organic acids.
Heat treatment capabilities enable engineers to tune mechanical qualities for particular applications, which is a significant advantage. During the annealing process, stress is reduced, and ductility is improved without reducing the material's resistance to corrosion. The annealing temperature for titanium sheets normally falls somewhere between 1200 and 1400 degrees Fahrenheit.
Welding titanium sheet offers joints that are reliable when the processes are followed correctly. Due to the limited thermal conductivity of the material, careful heat management is required; nonetheless, the end result is welds that are resistant to corrosion and strong, making them appropriate for use in the building of pressure vessels.
In large-scale installations, the benefits of weight reduction become significantly more substantial. While maintaining greater strength, titanium's density of 0.163 pounds per cubic inch, in comparison to the 0.29 pounds per cubic inch of stainless steel, results in a reduction in structural loads and transportation costs.
Chuanghui Daye's ASTM B 265 Titanium Sheet Advantages
When compared to traditional suppliers of titanium sheet, our manufacturing capabilities in China's "Titanium Capital" provide a number of noteworthy benefits. The use of sophisticated electron beam furnaces guarantees that all production batches will have a chemical composition that is consistent and that the material will be of excellent quality.
Through the use of the cold rolling method, ASTM B 265 titanium sheet thickness may be precisely controlled while maintaining tight tolerances. Traceability is guaranteed by our quality management system, which adheres to the standards of ISO 9001:2015. This system covers everything from the raw materials to the final inspection. A detailed testing procedure is performed on each sheet, which includes a verification of the tensile strength and an evaluation of the surface quality.
Custom cutting services remove unnecessary processing costs for end customers. We offer sheets that are cut to exact specifications at no additional cost, which saves both time and material by lowering the amount of material that is wasted. The flexibility offered by this feature is especially advantageous for research institutes and prototype development projects that require dimensions that are not standard.
We are able to provide technical support throughout the entire process of material selection thanks to our thirty years of experience in the sector. The engineers are provided with comprehensive data on the mechanical qualities, welding recommendations, and fabrication standards that are unique to the chemical processing applications they undertake.
A pricing system that is factory-direct avoids the markups that are added by distributors while still preserving premium quality. Compared to traditional titanium sheet suppliers in international markets, volume discounts make it possible for large-scale projects to be completed at prices that are more competitive.
Optimal Usage Guidelines for Maximum Benefits
When choosing a suitable grade, it is necessary to give careful consideration to the available operating circumstances as well as the performance requirements. For the majority of common chemical processing applications, Grade 2 is suitable for use in locations with moderate temperatures and standard corrosive conditions.
Grade 5 has outstanding tensile strength and fatigue resistance, making it an ideal material for high-pressure tanks and structural components. In applications that are particularly demanding and where safety issues are of the utmost importance, the increased mechanical qualities justify the greater cost.
ASTM B 265 titanium sheet fabrication processes that are done correctly optimize the benefits of the material. During the cutting and forming processes, it is important to guard against contamination from iron or steel tools. It is recommended to make use of titanium tooling or stainless steel equipment in order to avoid problems with galvanic corrosion.
Included in the recommendations for storage are settings that are clean, dry, and free of contact with carbon steel. Protective plastic covering eliminates the possibility of surface contamination, which could have an impact on the quality of welding or the resistance to corrosion.
When compared to steel, titanium has a lower modulus of elasticity, which should be taken into account during the design process. It is necessary for structural calculations to take into account this discrepancy in order to provide sufficient stiffness in load-bearing functions.
Prior to installation, quality inspection processes ensure that the titanium sheet standards are met. It is important to verify the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the mill by checking the test certificates. When performing chemical service, surface inspection is used to identify any faults that could potentially impact performance.
Critical Considerations for Chemical Processing Use
The constraints on temperature change depend on the grade and the application environment. In the majority of chemical conditions, pure titanium grades continue to exhibit outstanding characteristics up to 600 degrees Fahrenheit. There is a possibility that Grade 5 or specialist alloys will be required for optimal performance at higher temperatures.
Certain chemical processes are susceptible to the dangers posed by hydrogen embrittlement. There is a correlation between hydrogen absorption and decreased ductility, which can be caused by cathodic protection systems or surroundings with a high pH. The operational conditions should be monitored, and suitable preventative actions should be implemented.
When titanium comes into contact with other metals, it is important to pay attention to galvanic compatibility. Even though titanium is a noble metal, it has the ability to resist galvanic corrosion. However, when exposed to electrolytic solutions, titanium may speed up the corrosion of less noble materials such as aluminum or carbon steel.
The use of fluoride-containing substances should be avoided during cleaning procedures. Despite the fact that titanium is resistant to the majority of substances, it is quickly corroded by hydrofluoric acid and fluoride salts. If you want to keep the protective oxide layer intact, you should use cleaning solutions that are appropriate.
Because of the differences in thermal expansion coefficients between steel and other materials, mixed-material designs require careful study. There is a possibility that expansion joints or flexible connections will be required in order to accommodate differential movement in applications that involve temperature cycling.
Conclusion
ASTM B 265 titanium sheet provides unmatched benefits for chemical processing applications through superior corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical properties, and long-term reliability. The material's ability to withstand harsh chemical environments while maintaining structural integrity makes it an ideal choice for pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and process equipment. Chuanghui Daye's manufacturing expertise and quality commitment ensure consistent material performance for critical chemical processing applications. The combination of technical excellence, competitive pricing, and comprehensive support makes our titanium sheets the preferred solution for demanding industrial environments.
FAQ
Q: What makes Grade 2 titanium sheet ideal for chemical processing equipment?
A: Grade 2 offers excellent corrosion resistance in most chemical environments with good formability and weldability. The material resists chloride stress corrosion cracking and maintains integrity in acids, alkalis, and organic solvents commonly found in chemical processing.
Q: How does titanium sheet compare to stainless steel for chemical applications?
A: While titanium has higher initial costs, the total lifecycle value often favors titanium due to extended service life, reduced maintenance, and elimination of replacement needs. The superior corrosion resistance prevents costly equipment failures and production interruptions.
Q: Can ASTM B 265 titanium sheets be used in high-temperature chemical processes?
A: Yes, titanium maintains excellent properties at elevated temperatures. Grade 2 performs well up to 600°F, while Grade 5 handles higher temperatures with enhanced strength. The material's thermal stability makes it suitable for heat exchangers and high-temperature reactors.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Superior ASTM B 265 Titanium Sheet Supply
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye delivers premium titanium alloy sheets with guaranteed quality and competitive factory pricing. Our ISO 9001:2015 certification ensures consistent material properties and a reliable supply for your chemical processing projects. As an experienced ASTM B 265 titanium sheet manufacturer, we provide technical support, custom dimensions, and rapid delivery to meet your specific requirements. Contact us at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your titanium sheet applications and receive detailed quotations for your next project.
References
1. American Society for Testing and Materials. "Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate." ASTM B265-20, West Conshohocken, PA, 2020.
2. Boyer, Rodney R., and Harold L. Gegel. "Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications." Materials Park, OH: ASM International, 2019.
3. Lutjering, Gerd, and James C. Williams. "Engineering Materials and Processes: Titanium." 2nd Edition, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2018.
4. Peters, Manfred, and Christoph Leyens. "Titanium and Titanium Alloys in Chemical Process Industry." Chemical Engineering Progress, Vol. 115, No. 8, 2019.
5. Schutz, Roger W. "Corrosion of Titanium and Titanium Alloys in Chemical Processing Equipment." Materials Performance and Characterization, Vol. 8, No. 4, 2019.
6. Donachie, Matthew J. "Titanium: A Technical Guide for Chemical Processing Applications." 3rd Edition, Materials Park, OH: ASM International, 2020.