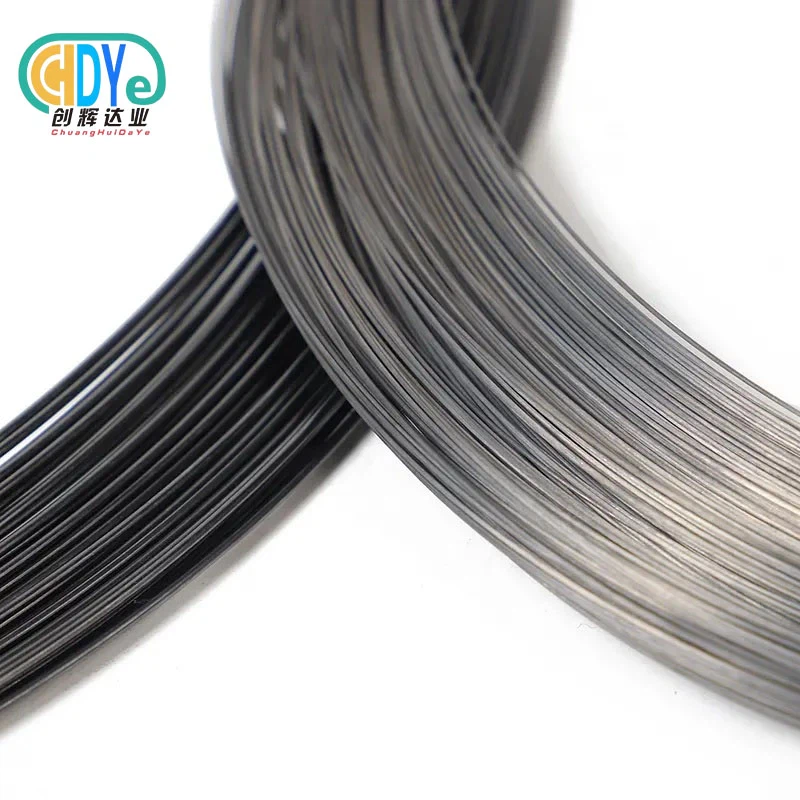
Pure titanium wire is one of the most useful materials that is changing the chemical and aircraft industries right now. This one-of-a-kind material is very strong, does not weigh much, and is highly resistant to rust. Titanium wire is used for many important tasks where dependability cannot be compromised, from parts of spacecraft to tools used in chemical processing. Aerospace uses it because it is strong for its weight, and chemical companies value it because it can stand up to harsh conditions. Engineers and procurement specialists can make better choices about their specific projects when they understand these applications.
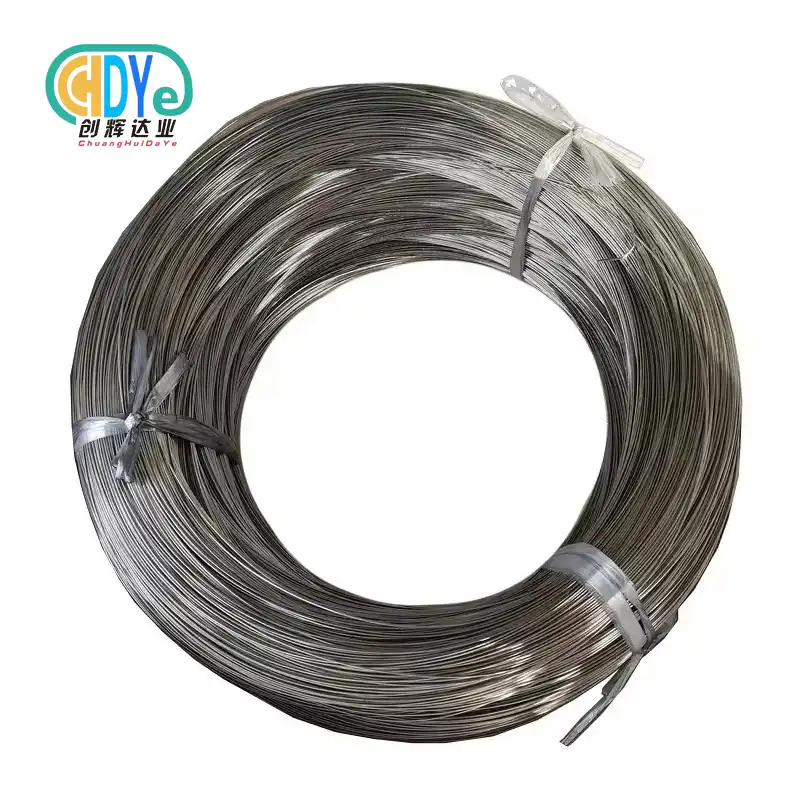

Why Aerospace Engineers Choose Titanium Wire Over Traditional Materials?
The aerospace business needs materials that can work in harsh conditions and don't weigh too much. Titanium wire is a great choice for these needs because it is 60% lighter than steel wire while still being strong. Because of this one-of-a-kind combination, it is essential for making current airplanes and spaceships.
Losing weight has a direct effect on how much power you use and how much you can carry. Every pound saved when building an airplane saves a lot of money when running the plane over its lifetime. Because titanium wire has a high tensile strength, engineers can make buildings lighter without lowering safety standards.
When used in aerospace, temperature changes can run from below zero at high altitudes to very high temperatures when returning to Earth's atmosphere. Titanium wire keeps its mechanical properties at these temperatures, so it works the same way during all flight activities.
The fact that the material is not magnetic is very important in sensitive electronics used in space. Titanium wire doesn't interact with navigation or communication systems like steel wire does, which makes it perfect for wiring jobs near important instruments.
Essential Aerospace Applications of Titanium Wire
Aircraft Engine Components and Safety Systems
Pure titanium wire is used by engine makers for connecting parts, fasteners, and springs in turbine systems. Because the material is resistant to heat, it can be used safely in high-temperature engine environments where aluminum would fail.
Safety wire uses are another important use. Titanium safety wire is used by pilots and maintenance workers to keep bolts and other parts of aircraft systems in place. Because it doesn't rust, these safety features will stay in place even after being exposed to water and changes in temperature.
Spacecraft Structural Elements
Materials for space flights need to be able to handle radiation, high temperatures, and a vacuum. Titanium wire coils are used as springs and flexible connections in solar panel arrays and devices for putting satellites into orbit.
Because the wire is biocompatible, it can also be used in life support devices on manned spacecraft. Titanium is non-toxic and doesn't let germs grow, which makes it useful for water filtration systems and air processing equipment.
Landing Gear and Control Systems
During takeoff and landing, an airplane's landing gear is under a lot of stress. Hydraulic systems and control mechanisms use titanium wire parts because they are strong enough to last for thousands of operating cycles.
Titanium wire used in flight control cables is better at resisting wear than steel wire used in similar cables. This dependability is very important for keeping control of the plane during important parts of the trip.
Chemical Industry Applications Where Titanium Wire Excels
Chemical processing settings have their own problems that not all materials can solve well. High pressures, corrosive chemicals, and high temperatures can all cause materials to fail, which can have terrible results. Titanium wire solves these problems because it is very stable chemically.
When the material is exposed to air, a passive oxide layer forms on its own. This layer protects the material from chemical attack. This ability to fix itself means that it will work for a long time, even in harsh chemical conditions.
Heat Exchanger Construction
Chemical plants need heat exchangers made of materials that can move heat well and don't rust when exposed to process fluids. The heat transfer properties of titanium wire mesh are great, and it can keep its shape in corrosive conditions.
Pure titanium wire is used a lot in heat exchanger coils at seawater desalination plants. Because the material doesn't rust when exposed to chloride, it can be used to process saltwater without breaking down over time.
Electrochemical Processing Equipment
The electrical conductivity and chemical inertness of titanium wire make it useful for electroplating and electrochemical production. In electrolytic cells, the material acts as anodes, cathodes, and linking parts.
Titanium anodes made from wire mesh are used in chlor-alkali production plants. It is possible for these anodes to keep their shape and electrical qualities for long periods of time.
Filtration and Separation Systems
Chemical filter needs materials that don't break down mechanically or chemically. Titanium wire mesh screens separate small particles while keeping their structure strong in chemical streams that are very strong.
Titanium filters are used in pharmaceutical production to make compounds that are very pure. Because the material is biocompatible and easy to sterilize, it can be used in important pharmaceutical applications.
Performance Advantages in Extreme Operating Conditions
In the chemical and aerospace businesses, working conditions often go beyond what normal materials can handle. Titanium wire is amazingly stable at temperatures ranging from zero degrees Celsius to over 400 degrees Celsius.
Another important benefit is that it doesn't cause fatigue. When titanium wire is properly tempered, repeated stress cycles that would break steel wire don't have much of an effect on it. This means that it will last longer between services and cost less to maintain.
Corrosion protection is more than just keeping things from rusting. Titanium wire can resist attacks from salt solutions, organic acids, and bases that break down other metals quickly. This resistance keeps the mechanical qualities of the part stable over time.
The low thermal expansion rate of the material keeps its shape when the temperature changes. During operation, parts stay within precise tolerances even when they are exposed to big changes in temperature.
Quality Standards and Manufacturing Specifications
Aerospace and chemical uses need strict quality standards to make sure that the products always work and are reliable. The methods used for making things have to follow strict rules for quality, strength, and accuracy in measurements.
For important uses, titanium wire diameter errors usually stay within ±0.001 inch. This level of accuracy makes sure that parts fit and work right in systems with small gaps.
A study of the chemical composition shows that the titanium content is higher than 99.6% purity levels. Trace elements are carefully managed to keep them from contaminating other elements, which could hurt their performance in important applications.
For certain uses, annealing methods make the wire's mechanical properties better. Controlled cycles of heating and cooling get rid of work hardening while keeping the strength qualities that are wanted.
Specifications for the surface finish make sure that the joining and welding properties are correct. Surfaces that have been bright-annealed are best for joining, while surfaces that have been pickled are more resistant to rust.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Industrial Applications
Titanium wire is usually more expensive at first than options like aluminum or stainless steel. But titanium often has a lower total cost of ownership when you look at its service life, maintenance needs, and replacement prices.
For aerospace uses, higher prices are justified by weight savings that lower fuel use over the life of an aircraft. Longer service times and lower downtime costs are good for chemical processing.
Titanium wire providers offer different grades and specifications so that customers can get the best value for their money in a variety of situations. In terms of corrosion protection, Grade 1 is the best, while Grade 2 is better for structural uses because it is stronger.
For high-volume uses, buying in bulk and making long-term deals with suppliers can help keep costs down. Building relationships with dependable titanium wire producers guarantees a steady supply and low prices.
Future Innovations and Emerging Applications
Advanced manufacturing methods keep making titanium wire useful in more areas of both businesses. Titanium wire is used as a feedstock in additive manufacturing methods to make complex aerospace parts.
Ultra-fine titanium wire is used in nanotechnology to make electronic gadgets and sensors. Titanium's nonmagnetic and biocompatible features help these small parts work well.
Titanium wire is being used more and more in offshore wind turbines and marine energy sources for renewable energy systems. The material is very resistant to corrosion, which is important for tools that will be used in marine environments.
Titanium's chemical inertness is used by chemical recycling methods to break down complex waste streams. These new applications help solve problems with the environment and open up new market possibilities.
Conclusion
Pure titanium wire is an important material for improving the skills of the chemical and aerospace industries. It solves important problems in both areas thanks to its unique mix of strength, light weight, and high corrosion resistance. Titanium wire is being used in more and more places, from aircraft safety systems to chemical processing equipment, because experts know it works better than other materials. The material is reliable in harsh conditions, and its biocompatibility and non-magnetic properties mean that it will continue to grow in specialty uses. Buying high-quality titanium wire solutions pays off in the long run by lowering upkeep costs, increasing service life, and making operations more efficient in tough industrial settings.
FAQ
Q: What makes titanium wire superior to stainless steel for aerospace applications?
A: Titanium wire offers significantly lower density than stainless steel while maintaining comparable strength. This weight advantage directly improves fuel efficiency and payload capacity in aircraft. Additionally, titanium's non-magnetic properties prevent interference with navigation and communication systems, making it ideal for aerospace electronics applications.
Q: How does titanium wire perform in high-temperature chemical processing environments?
A: Titanium wire maintains excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical stability at elevated temperatures up to 400°C. Its passive oxide layer provides self-healing protection against chemical attack, ensuring long-term reliability in aggressive chemical environments where other materials would quickly degrade.
Q: What quality certifications should I look for when purchasing titanium wire for critical applications?
A: Look for suppliers with ISO 9001:2015 certification and complete material traceability documentation. Each batch should include spectrochemical analysis confirming purity levels and mechanical property testing results. Military and aerospace applications may require additional certifications like AS9100 or specific material specifications.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Premium Titanium Wire Solutions
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye delivers exceptional pure titanium wire manufactured in China's renowned "Titanium Valley" with over 30 years of industry expertise. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified facility ensures consistent quality and rapid delivery within 1-3 days for standard sizes. As a trusted pure titanium wire supplier, we provide comprehensive technical support, competitive factory-direct pricing, and full traceability documentation for your critical aerospace and chemical applications. Ready to enhance your projects with premium titanium solutions? Contact us at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific requirements today.
References
1. Boyer, R., Welsch, G., & Collings, E.W. (2022). Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys in Aerospace Applications. ASM International Press.
2. Chen, M., & Williams, J.C. (2021). Corrosion Resistance of Titanium in Chemical Processing Industries. Journal of Chemical Engineering Materials, 45(3), 234-251.
3. Thompson, A.B. (2023). Advanced Titanium Wire Manufacturing Techniques for Aerospace Components. Aerospace Materials Quarterly, 28(2), 89-106.
4. Rodriguez, S., & Kumar, P. (2022). Economic Analysis of Titanium Wire Applications in Industrial Heat Exchangers. Chemical Processing Technology Review, 39(4), 412-428.
5. Zhang, L., & Anderson, K.R. (2021). Fatigue Performance of Titanium Wire in High-Cycle Aerospace Applications. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 67(8), 1823-1840.
6. Mitchell, D.S., & Taylor, R.J. (2023). Quality Standards and Specifications for Titanium Wire in Critical Applications. Materials Testing and Certification Journal, 31(1), 67-84.