- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Can Titanium Alloy Wire Be Used for Medical Devices?
In healthcare, titanium alloy wire is preferred for medical devices. Medical implants, surgical equipment, and therapeutic devices benefit from the titanium alloy wire's biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio. Medical-grade titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb are tested and certified for patient safety and device reliability in harsh biological conditions.
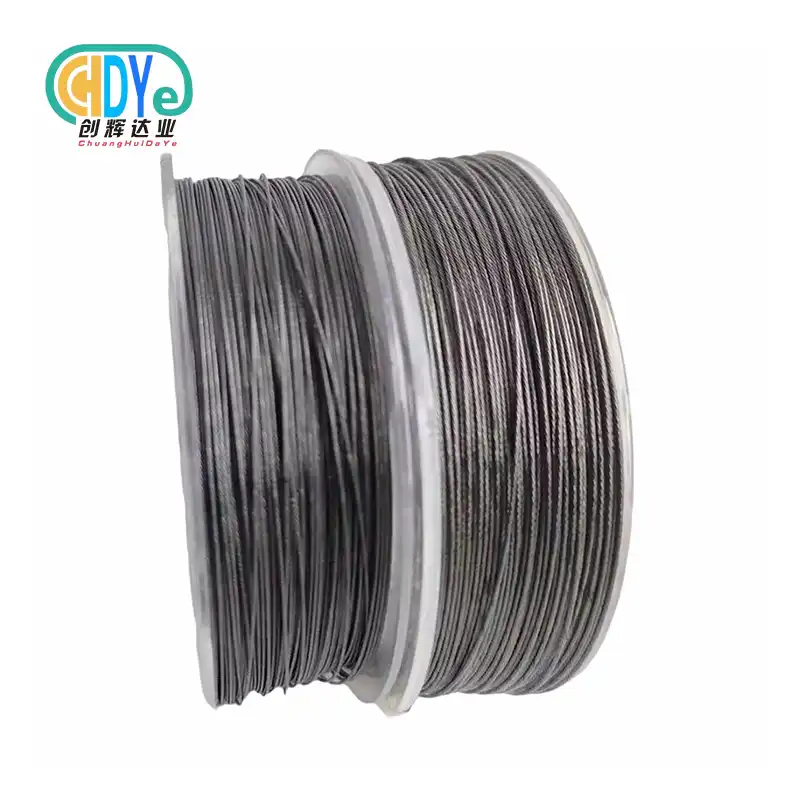

Understanding Titanium Alloy Wire in Medical Applications
Materials that can survive extreme bodily conditions while preserving structural integrity and safety are crucial to the medical device business. Titanium alloy wire is essential in this industry due to its unique metallurgical features and clinical efficacy.
Composition and Grades of Medical Titanium Alloys
Medical titanium alloys are balanced for healthcare purposes. The most popular alloy, Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5), has 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium for good mechanical qualities and corrosion resistance. Ti-6Al-7Nb, which replaces vanadium with niobium to prevent cytotoxicity, is another essential medicinal alloy. These alloys are strictly inspected throughout manufacture to ensure chemical and mechanical consistency.
Medical titanium alloys are developed for biocompatibility and load-bearing strength. Pure titanium grades (Grades 1-4) are used in medical applications that value corrosion resistance over mechanical strength. Each grade has benefits depending on the medical application and performance needs.
Essential Properties for Medical Applications
Medical device manufacture requires titanium alloy wire due to its important qualities. The material is biocompatible, integrating well with human tissue without producing biological responses. The stable oxide layer that titanium forms limits ion leakage into adjacent tissues.
Titanium alloy wire has a higher strength-to-weight ratio than stainless steel and better physiological corrosion resistance. This combination makes lighter, more comfortable medical equipment that is structurally reliable. Titanium alloys are non-magnetic, making them compatible with MRI scans.
Comparison with Alternative Materials
Titanium alloy wire outperforms stainless steel in long-term implant applications. Nickel and chromium in stainless steel may induce allergic responses in sensitive persons. Titanium alloys eliminate this problem and offer greater fatigue resistance under cyclic loads.
While nickel-based alloys have outstanding mechanical qualities, biocompatibility problems limit their usage in permanent implants. Though excellent for radiation shielding, tungsten wires lack the biocompatibility needed for most medical device applications. Titanium alloys have been used in orthopedic implants for decades, with success rates over 95%.
Manufacturing and Specification Standards of Titanium Alloy Wire for Medical Devices
Medical-grade titanium alloy wire is manufactured using complex methods to meet healthcare quality standards. Understanding these processes helps procurement experts choose materials and evaluate suppliers.
Production Process and Quality Control
Medical titanium alloy wire is made from high-purity titanium sponge and verified alloying materials. For homogeneous alloy composition and biocompatibility, vacuum arc remelting (VAR) or electron beam melting is used.
Wire drawing requires numerous passes through precision dies and interim annealing to maintain mechanical qualities. Chemistry, mechanical property, and microstructural tests are performed on each production lot. To document raw ingredients to final product delivery, manufacturers keep extensive traceability records.
Quality assurance processes ensure ±0.01mm diameter tolerances through 100% dimensional inspection using modern measurement devices. Specialised finishing methods ensure smooth, defect-free surfaces for medical purposes.
Medical-Grade Specifications and Certifications
International standards validate medical titanium alloy wire for healthcare purposes. The major specification for surgical implant Ti-6Al-4V alloy is ASTM F136, which defines chemical composition, mechanical qualities, and testing criteria. ISO 5832-3 standardizes the same substance internationally.
The ASTM F1267 standard covers Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy, which eliminates vanadium while preserving mechanical characteristics. Tensile strength, fatigue, and corrosion resistance testing in simulated body fluid conditions are required by these requirements.
Medical device manufacturers must maintain ISO 13485 quality management system certification. Certification assures that production methods meet strict medical device regulations and preserve product quality.
Technical Performance Benchmarks
Medical-grade titanium alloy wire must meet mechanical property standards for clinical reliability. Depending on heat treatment, Ti-6Al-4V wire has tensile strengths of 860-1200 MPa. Elongation values of 8-15% show good ductility for forming and fatigue resistance.
Crimped or coiled applications like cardiovascular stents and orthodontic equipment require flexibility. Titanium alloys' modulus of elasticity (110 GPa) fits human bone better than stainless steel, lowering stress shielding in orthopedic implants.
Thermal and electrical conductivity are crucial in medical applications. Titanium alloys have lower electrical conductivity than stainless steel, which might be useful in electrical isolation applications.
Advantages and Benefits of Using Titanium Alloy Wire in Medical Devices
Due to its performance benefits and clinical success, titanium alloy wire is increasingly used in medical device manufacturing. Medical device manufacturers can improve material selection by understanding these benefits.
Superior Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Titanium alloy wire resists biological corrosion better than other materials, extending gadget lifespan. When exposed to oxygen, the stable titanium oxide layer forms an impermeable barrier that blocks metal ion release. This trait is especially useful in permanent implant applications where device lifetime affects patient outcomes.
Clinical trials show titanium implants last over 20 years without deterioration. In chloride-rich environments like bodily fluids, pitting and crevice corrosion resistance ensures device function throughout the lifecycle. Durability lowers revision operations, decreasing healthcare expenditures and enhancing patient quality of life.
Titanium alloy wire can withstand autoclave cycles, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide sterilization, another benefit. This adaptability lets medical device designers choose the best sterilizing procedure without affecting material performance.
Lightweight Design and Enhanced Patient Comfort
Titanium alloys' low density allows lightweight medical devices that increase patient comfort and compliance. Titanium alloy wire orthopedic implants lower patient weight while maintaining structural integrity. This is especially useful in spinal fixation systems and joint replacement components, where weight reduction affects patient mobility and comfort.
Lightweight materials reduce blood vessel wall stress and increase hemodynamic performance in cardiovascular applications. Titanium alloy wire stents have excellent radial strength and smaller strut profiles, lowering restenosis risk and maintaining vessel patency.
The strength-to-weight advantage allows novel device designs that heavier materials could not. Longer minimally invasive surgical devices do not compromise physician control or tiredness during long procedures.
Biocompatibility and Safety Profile
Clinical and academic studies have shown that titanium alloy wire. Titanium alloys are hypoallergenic, eliminating nickel sensitivity and other metal sensitivities that might impair patient outcomes with other materials.
Titanium alloys' osseointegration allows orthopedic and dental implant bone connection. Stable interfaces from biological bonding improve implant stability and lifetime. Research shows that titanium surfaces enhance osteoblast adhesion and proliferation, facilitating natural bone remodeling.
Titanium and its alloys are non-toxic, as proven by decades of clinical use in varied patient populations. In diverse anatomical regions, tissue compatibility studies show low inflammatory response and excellent long-term acceptance.
Real-World Clinical Applications and Success Stories
Stents are one of the titanium alloy wires in medical devices. Radial strength, fatigue resistance, and biocompatibility allow drug-eluting stents to maintain vascular patency and deliver therapeutic drugs. Clinical trials show titanium-based coronary stents have success rates over 90%.
The adaptability of titanium alloy wire in load-bearing applications is shown by orthopedic implants. Titanium wire spinal fusion systems have great long-term stability and fusion rates equivalent to traditional materials while improving patient comfort. Hip and knee replacement systems use titanium alloy wire in cables and reinforcements.
Titanium alloy wire's non-magnetic and corrosion-resistant qualities aid endoscopic instruments. Titanium wire braided flexible endoscopes are compatible with all imaging modalities and have outstanding torque transmission and durability over thousands of use cycles.
Procurement Insights: Choosing and Buying Titanium Alloy Wire for Medical Devices
Titanium alloy wire providers are difficult for medical device manufacturers to choose from. Understanding important evaluation criteria and market trends helps buyers balance quality, cost, and supply chain reliability.
Supplier Evaluation and Quality Assurance Criteria
Procurement professionals must choose medical-grade titanium alloy wire providers based on quality management and regulatory compliance. Suppliers should be ISO 13485-certified and familiar with FDA and international medical device regulations. Complete traceability, material test certificates, and statistical process control data should be included in quality documentation.
Assessment of manufacturing competence should include production capacity, equipment sophistication, and technical expertise. In-house melting and processing suppliers have superior quality control and shorter lead times than distributors. Advanced testing equipment, including spectrometers, tensile testing machines, and metallographic analysis capability, shows quality assurance dedication.
Suppliers with audit readiness and transparency trust their quality systems. Top suppliers encourage customer audits and have thorough quality manuals that outline processes and responsibilities. Accredited organizations conduct third-party audits to ensure quality.
Market Analysis and Cost Considerations
Based on alloy composition, amount, and specification, titanium alloy wire prices vary greatly. Due to manufacturing complexity and alloying expenses, Ti-6Al-4V wire costs more than pure titanium. Due to low manufacturing volumes and complex processing, specialty alloys like Ti-6Al-7Nb cost more.
Volume purchases can save a lot, especially for high-consumption applications. Annual supply agreements frequently include price protection and priority distribution amid tight supply. To optimize the total cost of ownership, inventory carrying costs must be weighed against volume discounts.
Geography affects pricing and supply security. Domestic suppliers may give quality assurance and regulatory compliance, while international sources may offer cost savings. Supply chain diversification reduces single-source dependency hazards.
Customization Capabilities and Technical Support
Suppliers must customize wire arrangements for medical device applications. Suppliers with modern wire drawing equipment can make custom diameters, tempers, and finishes. Custom straightening, cutting, and packaging increases value for medical device producers.
Technical support distinguishes leading from commodity vendors. Metallurgical expertise, application engineering support, and regulatory guidance enable medical device manufacturers choose and process materials. Technical libraries and material property data from suppliers aid product development.
Prototyping and sample programs provide extensive evaluation before bulk procurement. Suppliers supplying free samples and speedy prototypes show product confidence and client success.
Delivery Terms and Supply Chain Reliability
Medical device manufacturing requires reliable material availability to fulfill production and regulatory requirements. Standard grades can be delivered quickly by suppliers with inventory programs, but unique standards take longer. Delivery delays can be avoided by understanding supplier capacity limits and production scheduling.
Emergency supplies are essential in case of equipment failures or demand spikes. Suppliers with flexible production scheduling and expediting help in difficult situations. Order monitoring and clear communication assist in managing expectations and planning.
International shipment requires packaging, documentation, and customs clearance. Expert suppliers help with international transactions with material identification and regulatory compliance documentation.
Our Expertise in Titanium Alloy Wire Manufacturing and Supply
After decades of expertise and innovation, Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. is a leading medical-grade titanium alloy wire producer and supplier. Baoji, China's "Titanium Capital," offers our organization unmatched raw material access and technical competence.
Company Background and Manufacturing Excellence
Our manufacturing plant uses old metallurgical skills and current production technologies to make titanium alloy wire for the most demanding medical devices. An industry specialist with over 30 years of rare metal processing experience started the company, recognizing medical application technological problems and quality needs.
We use electron beam and vacuum arc furnaces to melt alloys with ultra-high purity and consistency. The multi-pass wire drawing technique achieves ±0.01mm dimensional accuracy with precision dies and intermediate annealing processes, ensuring superior mechanical qualities.
ISO 9001:2015 quality management systems promote consistent production and thorough documentation. Chemical, mechanical, and dimensional tests are done on every production lot before release. Our traceability systems document raw material receipt to delivery.
Product Range and Customization Options
Our medical-grade titanium alloy wire product line includes many alloys and combinations for various medical device needs. Standard wires include Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) and Ti-6Al-7Nb in 0.1mm to 6.0mm diameters. For certain applications, straight and coiled variants are offered.
We can develop custom alloys for medicinal uses. Our metallurgical team collaborates with customers to improve alloy chemistry for biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and shape memory.
Bright annealed, pickled, and polished finishes fulfill different application needs. Sterile applications can use individual coil packaging and inert environment protection.
Quality Assurance and Certification Compliance
Through rigorous testing and documentation, our quality assurance methodology exceeds industry standards. Chemical analysis using modern spectrometric instruments controls alloy composition. Every production lot undergoes tensile, elongation, and fatigue resistance testing.
Certified laboratories undertake cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation investigations to determine biocompatibility for medical uses. Our materials always meet USP Class VI and ISO 10993 biological evaluation standards.
Complete material test certifications, dimensional inspection reports, and biocompatibility test findings are certified. All paperwork is provided in hard copy and electronic format to support client regulatory submissions and quality system needs.
Customer Support and Global Supply Chain
Technical specialists with medical device industry experience assist with application guidance and material selection in our customer service team. Customers use engineering support to optimize processing parameters and solve application issues.
Established shipping partnerships and full export documentation services ensure reliable delivery worldwide. Standard stocking strategies keep common grades and sizes available for 1-3 day delivery. Custom specs take 7-15 days to produce and ship.
Customers can try our materials for free before ordering. Sample packages support full examination and testing with detailed documentation and technical data.
Conclusion
Titanium alloy wire has been used in medical devices for decades due to its clinical success and technological improvement. Its biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance make it ideal for cardiovascular stents and orthopedic implants. As medical device technology advances, titanium alloy wire will help improve patient outcomes and healthcare innovation.
FAQ
Q: What sterilization methods are compatible with titanium alloy wire?
A: Titanium alloy wire is compatible with all standard medical device sterilization methods, including steam autoclaving, gamma radiation, electron beam sterilization, and ethylene oxide gas sterilization. The stable oxide layer on titanium surfaces remains intact through repeated sterilization cycles, maintaining material properties and biocompatibility throughout the device lifecycle.
Q: Which titanium alloy grades are most suitable for implantable medical devices?
A: Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) and Ti-6Al-7Nb are the most commonly used titanium alloys for implantable medical devices. Ti-6Al-4V offers excellent mechanical properties and hasan extensive clinical history, while Ti-6Al-7Nb provides similar performance without vanadium content, addressing potential biocompatibility concerns for long-term implant applications.
Q: How does titanium alloy wire compare to stainless steel in terms of cost and durability?
A: While titanium alloy wire typically costs 3-5 times more than stainless steel initially, its superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility often result in a lower total cost of ownership for medical applications. The extended device lifespan and reduced revision surgery requirements offset the higher material costs, particularly in permanent implant applications.
Q: Can titanium alloy wire be used in MRI-compatible medical devices?
A: Yes, titanium alloy wire is completely MRI-compatible due to its non-ferromagnetic properties. Unlike stainless steel or cobalt-chrome alloys, titanium does not create imaging artifacts or experience heating during MRI procedures, making it ideal for permanent implants that may require post-operative imaging.
Q: What quality certifications should I look for when purchasing medical-grade titanium alloy wire?
A: Look for suppliers maintaining ISO 13485 certification for medical device manufacturing, along with materials certified to ASTM F136 (Ti-6Al-4V) or ASTM F1267 (Ti-6Al-7Nb) standards. Additional certifications like FDA registration and CE marking demonstrate commitment to regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Premium Medical-Grade Titanium Alloy Wire
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye delivers exceptional medical-grade titanium alloy wire solutions backed by three decades of industry expertise and ISO 9001:2015 certification. Our comprehensive product range includes Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb wires in both straight and coiled configurations, with free samples available for evaluation. As a trusted titanium alloy wire manufacturer, we combine competitive factory-direct pricing with rapid delivery capabilities, maintaining stock inventory for 1-3 day shipment of standard specifications. Contact our technical team at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific medical device requirements and discover how our precision-engineered titanium alloy wire can enhance your product performance and regulatory compliance.
References
1. Long, M. and Rack, H.J. "Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—a materials science perspective." Biomaterials, Vol. 19, No. 18, 1998, pp. 1621-1639.
2. Niinomi, M. "Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications." Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, Vol. 1, No. 1, 2008, pp. 30-42.
3. Steinemann, S.G. "Metal implants and surface reactions." Injury, Vol. 27, Supplement 3, 1996, pp. 16-22.
4. Williams, D.F. "Titanium for Medical Applications." Titanium in Medicine, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2001, pp. 13-24.
5. Rack, H.J. and Qazi, J.I. "Titanium alloys for biomedical applications." Materials Science and Engineering C, Vol. 26, No. 8, 2006, pp. 1269-1277.
6. Geetha, M., Singh, A.K., Asokamani, R., and Gogia, A.K. "Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants – A review." Progress in Materials Science, Vol. 54, No. 3, 2009, pp. 397-425.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email