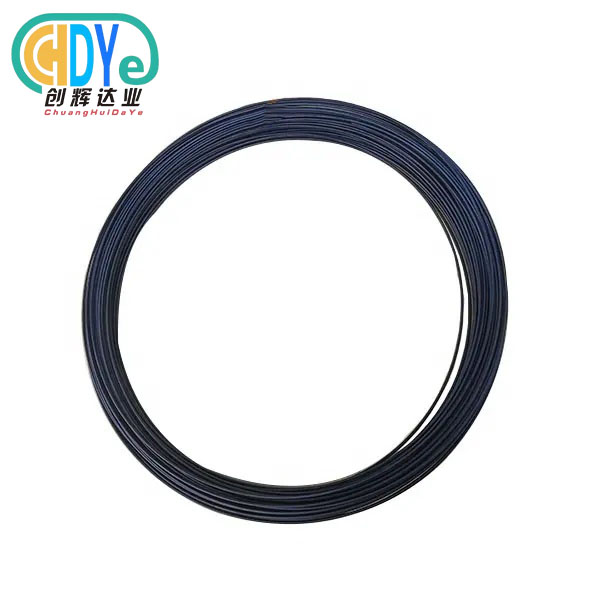
Tantalum niobium alloy wire parameters typically fall within the range of 0.3mm to 3mm in diameter. These wires correspond to the criteria set forth by ASTM B 365, and for applications that are considered important, they have precise tolerances of ±0.05mm. This combination, known as R05240 (Ta-40Nb), provides optimum ductility while also preserving high-temperature stability. The tolerances that are used in manufacturing are different depending on the diameter of the wire, with finer wires requiring more stringent controls during the drawing phase. A suitable selection of materials for applications in aerospace, chemical processing, and electronic component manufacturing can be ensured by having a thorough understanding of these diameter parameters.

Understanding Ta-40Nb Wire Composition and Properties
The designation R05240 is given to an alloy that has been properly manufactured to contain sixty percent tantalum and forty percent niobium. This alloy is used to create a superalloy wire that possesses remarkable performance qualities. This composition strikes a balance between the improved ductility of niobium and the corrosion resistance of tantalum. When compared to alternatives made of pure tantalum niobium alloy wire, the material that was produced possesses greater mechanical qualities.
The levels of chemical purity can reach a minimum of 99.9% or 99.95%, depending on the needs of the application. Manufacturing semiconductors and producing medical implants both require high-purity requirements, which are becoming increasingly important. Because of the regulated composition, the electrical conductivity and thermal stability of the wire are maintained consistently across a wide range of wire sizes.
Vacuum arc melting, electron beam remelting, and controlled atmosphere processing are all examples of manufacturing processes. By utilizing these procedures, contamination can be eliminated while simultaneously ensuring that the alloy is distributed uniformly across the wire cross-section. Quality control steps are implemented to ensure that the composition is accurate within the tolerance limit of ±0.1%.
Standard Diameter Specifications and Manufacturing Tolerances
ASTM B 365 establishes comprehensive guidelines for tantalum niobium alloy wire dimensions and tolerance requirements. Standard diameter ranges accommodate diverse industrial applications while maintaining manufacturing feasibility. Wire drawing operations require precise die control to achieve specified tolerances consistently.
Diameter specifications include:
- 0.3mm - 0.8mm: Ultra-fine applications with ±0.02mm tolerance
- 0.8mm - 1.5mm: General purpose with ±0.03mm tolerance
- 1.5mm - 3.0mm: Structural applications with ±0.05mm tolerance
The standards for the surface finish are complementary to the dimensional parameters. When it comes to electronic applications, wire surfaces should have Ra values that are lower than 0.4 micrometers. Surface quality standards are frequently required to be much more stringent in aerospace specifications. Lubricants used for drawing and annealing cycles have a considerable impact on the surface properties of the final product.
Measurement verification is accomplished by the utilization of laser diameter gauges and precision micrometers. Throughout the entirety of production runs, statistical process control ensures that tolerance compliance is maintained. Dimensional certificates that are fully traceable are included in the documentation for the purpose of quality assurance.
Wire Drawing Process and Quality Control Methods
Through the use of sequential die reductions, the wire drawing process involves the transformation of rod stock with a greater diameter into precise wire. While the material is being worked, the diameter is decreasing with each successive drawing stage. The ductility of the material is restored by intermediate annealing cycles, which also prevent cracking during the following processes.
Ensuring that the alloy's characteristics are preserved during the annealing process requires careful temperature management. Annealing in a vacuum furnace allows for uniform heating while also preventing oxidation from occurring. The grain structure and mechanical qualities of the finished wire are influenced by the cooling rates and temperatures.
At each stage of the processing, quality control checkpoints are used to monitor the dimensional accuracy. Measurements taken in real time identify variations before they happen to go above the tolerance limits. As part of the corrective actions, the changes and alterations to the process parameters are implemented.
The mechanical strength, elongation, and electrical resistivity of a material are validated by the testing of substance qualities. The yield strength is confirmed to satisfy the criteria of the specification through tensile testing. The grain size and phase distribution homogeneity can be verified by the use of microstructural analysis.
Application-Specific Diameter Selection Guidelines
Applications in the aerospace industry often demand wire sizes ranging from 0.5 millimeters to 2.0 millimeters for structural components and fastening systems. Due to their high strength-to-weight ratios, these standards are perfect for components that are used in aviation engines. Alloy qualities that are resistant to corrosion offer dependable performance in environments that are difficult to work with.
When it comes to heating elements and support structures, chemical processing equipment often makes use of greater dimensions (ranging from 1.5mm to 3.0mm). Because of their resistance to oxidation, TaNb alloys often have a longer service life when exposed to acidic conditions. Controlling the diameter of the wire mesh in a consistent manner and having flexible metal wire qualities are both beneficial to applications.
The applications of precision wire winding require ultra-fine wires with a diameter ranging from 0.3mm to 0.8mm for electronic components. Integration of medical devices is made possible by the biocompatible qualities of alloys. When vacuum systems are used, the electrical conductivity does not change regardless of the temperature changes.
Custom sizes that are not in accordance with standard sizes are frequently required by research institutions. The capabilities of small-batch production allow for the development of prototypes and the fulfillment of unique research requirements. Methods of production that are flexible are beneficial to the development of creative applications in developing technologies.
Tolerance Requirements for Critical Applications
Precision applications in the semiconductor manufacturing industry demand diameter tolerances that are exceedingly tight. Variations that exceed ±0.01mm have the potential to impact both the performance of components and the assembly procedures. In order to guarantee conformity with these strict requirements, advanced measurement techniques are utilized.
Both dimensions, precision and surface quality control, are required in order to meet the guidelines for medical implant wire standards. Testing for biocompatibility verifies that a material is safe for use in applications that involve human touch. Sterilization procedures must not have an impact on the mechanical qualities or dimensional stability of the material.
Applications that operate at high temperatures are subject to thermal expansion effects, which also have an effect on the effective wire diameter. Temperature-dependent dimension changes are something that must be taken into account in design calculations. Information regarding the coefficient of thermal expansion is used to inform the appropriate allocation of tolerance for particular operating conditions.
In order to achieve accurate control of the heat input, welding and joining procedures require wire diameters that are consistent. Automatic feeding systems are dependent on having dimensions that are consistent in order to function reliably. In industries that are subject to regulations, quality documentation helps to support traceability requirements.
Manufacturing Capabilities and Custom Processing Services
Manufacturing facilities of the modern era combine the more conventional methods of wire drawing with the most cutting-edge manufacturing control systems. Equipment that is controlled by a computer ensures that the quality remains consistent even when producing big quantities. Flexibility in production scheduling allows for the fulfillment of both standard and individualized diameter requirements.
Services for custom processing include annealing cycles, surface treatments, and package configurations that are specifically designed for the customer. Increasing the handling characteristics of automated assembly processes is accomplished by wire straightening operations. Not only do cutting and forming services provide value, but they also reduce the amount of client processing that is required.
The technical support teams provide assistance with the selection of materials and the formulation of specifications. Customers benefit from the guidance of engineering experience when navigating complicated application requirements. It is possible to quickly evaluate new designs and concepts thanks to the capabilities of rapid prototyping.
In order to meet the ongoing manufacturing requirements, supply chain management assures the reliable availability of materials. The reduction of lead times for standard specifications is achieved by strategic inventory positioning. In order to efficiently meet the expectations of worldwide customers, global shipping capabilities are required.
Conclusion
The success of the manufacturing process and the performance of the application are directly impacted by the correct selection of the diameters and tolerances of the tantalum niobium alloy wire. The ability to make informed material decisions is enabled by having a thorough understanding of the ASTM B 365 specifications, tolerance requirements, and quality control systems. For applications that are particularly demanding in the aerospace, chemical, and electronic industries, the R05240 formulation offers the best possible qualities. In order to guarantee a dependable supply of precision wire products that are in accordance with the exact specifications and delivery requirements, professional technical support and accredited manufacturing techniques are utilized.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Premium TaNb Wire Solutions
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye delivers precision-engineered tantalum niobium alloy wire with guaranteed dimensional accuracy and superior quality control. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing processes ensure consistent performance across all diameter specifications. As an experienced tantalum niobium alloy wire manufacturer, we provide comprehensive technical support and competitive factory-direct pricing for your critical applications. Contact us at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific wire diameter and tolerance requirements.
References
1. ASTM International. "Standard Specification for Tantalum and Tantalum Alloy Rod and Wire." ASTM B 365-18, West Conshohocken, PA, 2018.
2. Reed, R.C. "The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications - Tantalum-Niobium Systems." Cambridge University Press, Materials Science Monographs, 2006.
3. Pollock, T.M. and Tin, S. "Nickel-Based Superalloys for Advanced Turbine Engines: Chemistry, Microstructure, and Properties." Journal of Propulsion and Power, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2006.
4. Boyer, R., Welsch, G., and Collings, E.W. "Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium and Refractory Metal Alloys." ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1994.
5. Schulson, E.M. "The Mechanical Properties of Refractory Metal Wire: A Review of Drawing Effects and Annealing Behavior." Metallurgical Transactions A, Vol. 8A, 1977.
6. Northcott, L. "Molybdenum and Its Alloys: Including Tantalum-Niobium Systems." Academic Press Materials Science Series, London, 1956.