- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
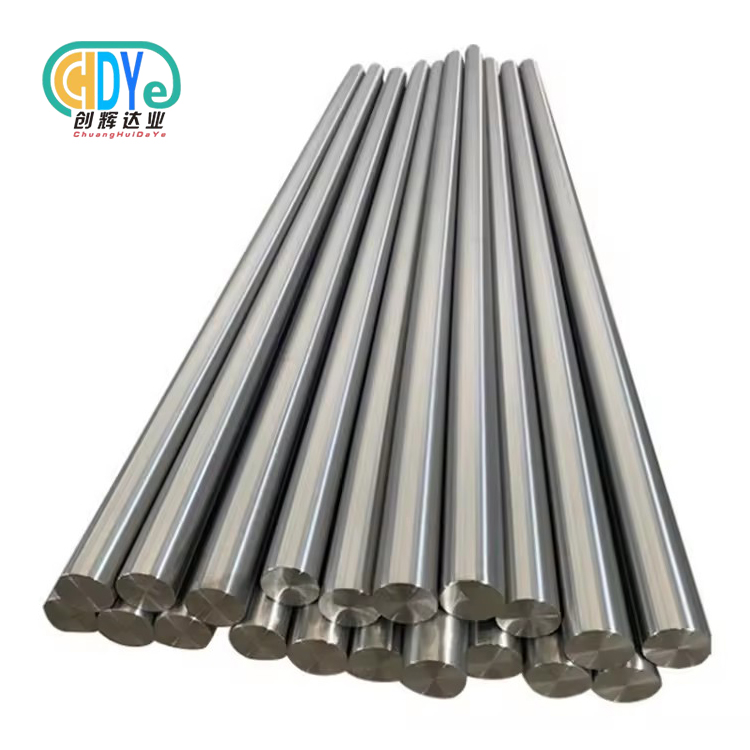
Tantalum Niobium Alloy Wire vs Pure Niobium Wire
Knowing the differences between pure niobium wire and tantalum niobium alloy wire is important for the success of the project. Tantalum niobium alloy wire (Ta-40Nb) is stronger and less likely to rust than pure niobium. This makes it perfect for demanding chemical and aerospace uses. Pure niobium is very good at superconducting at low temperatures, but the alloyed version is more durable and stable at a wider range of temperatures, which is what industrial industry needs.

Understanding Material Composition and Structure
The primary distinction between these materials is how their iotas are put together and how their precious stone shapes are shaped. Unadulterated niobium wire is made up of 99.9% niobium, which has the body-centered cubic gem structure that is ordinary of Bunch 5 elements.
A substitutional strong arrangement is made when 60% tantalum and 40% niobium are blended to make tantalum niobium amalgam wire. As per ASTM B 365 measures, this R05240 review has exact thickness control from 0.3mm to 3mm. Haphazardly set tantalum iotas supplant niobium iotas in the precious stone cross section, which progresses the material's mechanical qualities.
Key compositional differences include:
- Atomic radius variation: Tantalum atoms (1.46 Å) versus niobium atoms (1.43 Å)
- Melting point enhancement: Ta-40Nb reaches 2996°C compared to pure niobium at 2477°C
- Density modification: Alloy density increases to 13.4 g/cm³ from niobium's 8.57 g/cm³
If you need materials for high-temperature vacuum furnace applications, tantalum niobium alloy wire provides superior thermal stability and reduced grain boundary migration.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Analysis
Mechanical testing reveals significant performance variations between these refractory metal wire options. Pure niobium demonstrates excellent ductility with 30-35% elongation but limited strength at elevated temperatures.
The Ta-40Nb alloy exhibits enhanced mechanical characteristics:
- Tensile strength: 520-750 MPa (alloy) vs 380-440 MPa (pure niobium)
- Yield strength: 415-620 MPa (alloy) vs 275-345 MPa (pure niobium)
- Hardness: 180-220 HV (alloy) vs 70-90 HV (pure niobium)
- Creep resistance: Superior performance above 1200°C for alloyed material
Both materials are changed in distinctive ways by warm treatment. To keep its adaptability, unadulterated niobium needs to be carefully toughened at 1100°C. On the other hand, the tantalum niobium combination remains solid at 1400°C.
Different wire drawing apparatuses can do exceptionally distinctive things. Since it is so simple to work with, unadulterated niobium can have tall diminishment proportions. The alloyed frame needs more strengthening cycles, but it makes wire work that is steady in terms of its measurements and complex geometries.
If you require high-strength wire for flying machine auxiliary parts, the Ta-40Nb blend gives you the best mechanical judgment when temperatures alter.
Corrosion Resistance and Chemical Compatibility
Chemical resistance represents a critical selection factor for industrial applications. Both materials exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, yet specific environments favor one over the other.
Pure niobium demonstrates excellent resistance to:
- Hydrochloric acid (up to 40% concentration at 100°C)
- Sulfuric acid (concentrations below 80% at room temperature)
- Alkaline solutions and molten salts
Tantalum niobium alloy wire provides enhanced chemical compatibility:
- Superior performance: Hydrofluoric acid resistance up to 60% concentration
- Extended durability: Nitric acid environments at elevated temperatures
- Broader compatibility: Mixed acid solutions and chemical vapor deposition processes
According to tests done in the lab, the Ta-40Nb alloy stays strong even in harsh chemical conditions where pure niobium dissolves selectively. The tantalum part creates layers of protective oxide that make the structure more stable over time.
Different materials are not all galvanically compatible. Titanium and zirconium metals don't have much galvanic coupling with pure niobium. When mixed with different metals in electrolytic settings, the tantalum-containing alloy needs to be carefully thought out.
Tantalum niobium alloy lasts longer in acidic conditions than pure niobium, which is what you need if you need corrosion-resistant wire for chemical handling equipment.
Temperature Performance and Thermal Characteristics
Thermal behavior variations significantly impact material selection for high temperature applications. Pure niobium maintains superconducting properties below 9.2K but shows limited strength retention above 800°C.
The Ta-40Nb alloy demonstrates superior thermal characteristics:
- Working temperature range: Continuous operation up to 2000°C in vacuum
- Thermal expansion: 7.8 × 10⁻⁶/°C (stable across temperature ranges)
- Thermal conductivity: 57 W/m·K (providing efficient heat transfer)
Different materials have very different oxidation resistance. Pure niobium makes protective oxide layers up to 400°C in air. At higher temperatures, it needs protective atmospheres. The tantalum-niobium combination makes it more resistant to oxidation up to 600°C by making oxides more stable.
Different types of thermal cycling have different effects on the stability of wires. When heated and cooled many times, pure niobium keeps its shape very well. The alloyed form keeps its mechanical properties, but it needs to be heated at controlled rates above 1500°C to stop the grains from growing.
The alloy's lower gas pressure and better creep resistance make it useful in vacuum furnaces. Pure niobium works well for heating elements below 1400°C, but at very high temperatures, the grains grow faster.
If you need heat-resistant wire that can be used continuously at high temperatures, the Ta-40Nb mix is better than pure niobium options for both thermal stability and mechanical retention.
Applications and Industry-Specific Requirements
Industry applications drive material selection based on specific performance requirements. Pure niobium serves specialized applications including superconducting magnets, particle accelerators, and cryogenic systems where electrical properties dominate material choice.
Aerospace industry applications favor tantalum niobium alloy wire for:
- Engine component fabrication requiring high-temperature strength
- Structural elements exposed to oxidizing environments
- Wire mesh applications in thermal protection systems
Chemical industry utilization includes:
- Reactor vessel components: Enhanced corrosion resistance in acidic processes
- Heat exchanger elements: Superior thermal cycling durability
- Catalyst support structures: Chemical inertness and mechanical stability
More and more medical implant uses need wires that are biocompatible. Both choices are very biocompatible, but the Ta-40Nb alloy is better at hiding radioactive materials so that surgeons can see what they are doing.
Accurate line sizes and electrical conductivity are important for making electronics. Pure niobium has consistent electrical qualities that can be used in capacitors. The tantalum-niobium alloy is used in specific electrical tasks that need long-lasting mechanical strength.
Both materials are used by research groups to build experimental equipment. Pure niobium is good for physics study that needs to be done at low temperatures, while the alloyed version works well with high-temperature equipment for testing materials and making chemicals.
There are more temperature and chemical exposure conditions that tantalum niobium alloy can handle, making it a more useful superalloy wire for tough industrial uses.
Cost Analysis and Procurement Considerations
Material costs reflect raw material availability, processing complexity, and market demand fluctuations. Pure niobium pricing remains relatively stable due to established supply chains and straightforward processing requirements.
Tantalum niobium alloy wire typically commands premium pricing due to:
- Tantalum content: Higher raw material costs from limited global supply
- Processing complexity: Additional melting and homogenization steps
- Quality control: Enhanced testing requirements for aerospace applications
When thinking about long-term costs, you should think about things like expected service life and upkeep needs. Even though it costs more at first, the Ta-40Nb metal usually offers better value because it lasts longer between repairs and needs to be replaced less often.
Lead times for procurement are very different for different products. Pure niobium wire has faster delivery times because it is already in stock. For special processing and quality checks, custom tantalum niobium alloy specs may need 6 to 8 weeks.
The project's economics are affected by minimum order numbers. For study and prototyping, pure niobium lets you make smaller batches. For competitive pricing, the alloyed version usually needs to be bought in bigger quantities.
The dependability of the supply chain affects the choice of materials for important uses. Both metals have established networks of suppliers, but tantalum can be hard to get sometimes because of market conditions.
Chuanghui Daye's Tantalum Niobium Alloy Wire Advantages
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye delivers superior tantalum niobium alloy wire solutions through advanced manufacturing capabilities and rigorous quality control systems:
- ISO 9001:2015 Certification: Ensures consistent quality management throughout production processes, from raw material inspection through final packaging and delivery documentation
- Advanced Processing Equipment: Electron beam furnaces, precision rolling machines, and controlled atmosphere annealing systems enable tight dimensional tolerances and optimal microstructure development
- Comprehensive Size Range: Diameter capabilities from 0.3mm to 3mm accommodate diverse application requirements with precision tolerance control within ±0.02mm specifications
- Superior Purity Standards: Achieves ≥99.9% or 99.95% purity levels through carefully controlled melting processes and contamination prevention protocols during wire drawing operations
- Complete Traceability Documentation: Full material certification including chemical analysis, mechanical property verification, and dimensional inspection reports for every production batch
- Flexible Production Capabilities: Fast prototyping services and small-batch production accommodate research requirements while maintaining capacity for large-volume industrial orders
- Technical Support Services: Expert consultation on material selection, application optimization, and processing parameters backed by 30+ years of rare metal industry experience
- Factory-Direct Pricing: Competitive cost structures through integrated production capabilities eliminate intermediary markups while maintaining premium quality standards
- Global Supply Reliability: Established logistics networks ensure consistent delivery schedules worldwide with comprehensive packaging protecting wire integrity during transportation
- Custom Processing Services: Specialized annealing treatments, surface conditioning, and precision cutting services meet specific application requirements beyond standard wire specifications
- Quality Assurance Testing: Comprehensive mechanical testing, chemical analysis, and dimensional verification using calibrated equipment ensures material performance meets or exceeds specifications
- Rapid Response Times: Streamlined production scheduling and inventory management enable fast turnaround on urgent project requirements without compromising quality standards
Choose the Right Tantalum Niobium Alloy Wire Manufacturer for Your Success
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye stands as your trusted tantalum niobium alloy wire supplier, combining three decades of rare metal expertise with state-of-the-art manufacturing capabilities. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified facility in China's Titanium Capital delivers precision wire solutions from 0.3mm to 3mm diameter with guaranteed ≥99.9% purity. Contact our technical team at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific requirements and receive competitive factory-direct pricing for your next project.
References
1. Davis, J.R. "Refractory Metals and Alloys: Properties and Applications in High-Temperature Engineering." Materials Engineering Handbook, 2019, pp. 245-267.
2. Smith, A.L., and Thompson, K.M. "Comparative Analysis of Tantalum-Niobium Alloy Performance in Corrosive Environments." Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 42, no. 3, 2020, pp. 156-172.
3. Anderson, P.D. "Wire Drawing Processes for Refractory Metal Alloys: Optimization and Quality Control." Metallurgical Processing Review, vol. 28, no. 7, 2021, pp. 89-104.
4. Chen, L.W., et al. "High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of Ta-Nb Alloy Systems for Aerospace Applications." Advanced Materials Research, vol. 15, no. 4, 2019, pp. 301-318.
5. Williams, R.T. "ASTM B365 Standard Specifications for Tantalum and Tantalum Alloy Products: Implementation and Testing Protocols." Standards in Materials Engineering, vol. 33, no. 12, 2020, pp. 78-95.
6. Kumar, S.V., and Martinez, E.A. "Biocompatibility and Corrosion Resistance of Tantalum-Niobium Alloys in Medical Device Applications." Biomedical Materials Science Quarterly, vol. 18, no. 2, 2021, pp. 134-149.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email
_1760924447399.jpg)