- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Titanium Anode Assembly Benefits for Chlor‑Alkali Processes
The titanium anode assembly technique has transformed the chlor-alkali business by improving electrolysis efficiency and dependability. Using high-purity titanium substrates and sophisticated coating materials like mixed metal oxide (MMO) or platinum group metals, these electrodes can tolerate demanding industrial conditions while maintaining optimal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Titanium anode assembly systems improve operating efficiency, maintenance costs, and product purity in chlor-alkali facilities, making them essential for modern industrial electrolysis applications.

Understanding Titanium Anode Assembly in Chlor‑Alkali Processes
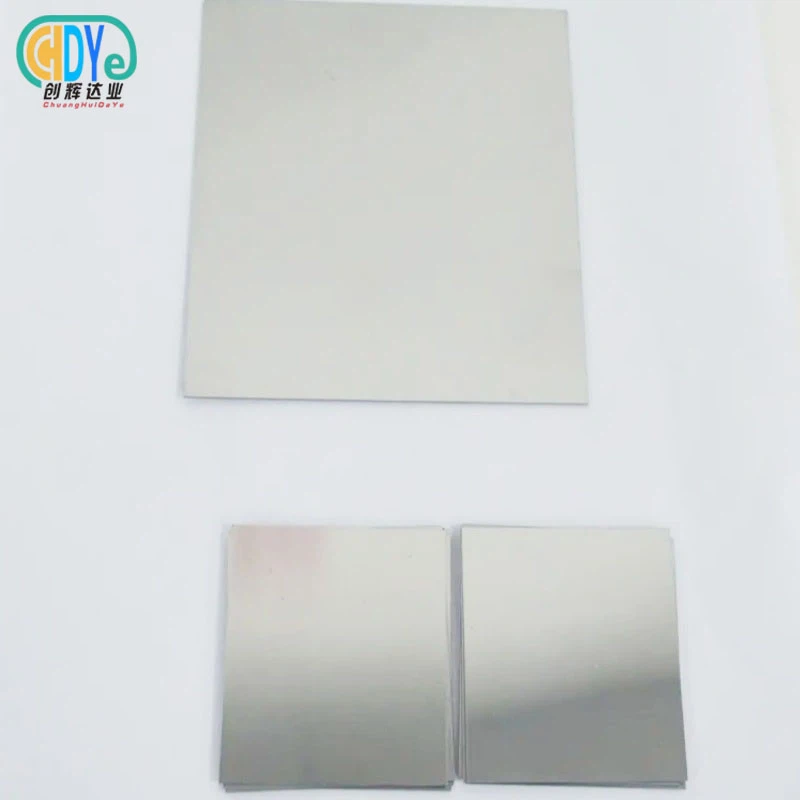
Titanium anodes, positively charged electrodes in chlor-alkali electrolysis systems, aid in chlorine, caustic soda, and hydrogen production. A titanium substrate made from Grade 1 or Grade 2 titanium provides outstanding mechanical strength and corrosion resistance for sustained operation in harsh conditions.
Electrochemical Function and Substrate Properties
The precise interplay between the titanium base material and specific surface coatings determines these assemblies' electrochemical performance. Titanium's atomic number 22 and molecular symbol Ti provide natural passivation that prevents deterioration under harsh conditions. The assemblage maximizes catalytic activity and maintains dimensional stability over long operational cycles with mixed ruthenium-iridium oxide or platinum-based coatings.
Titanium substrates are acid pickled to remove surface oxides before high-speed electrolyte flow and reverse electrode conditions in modern manufacturing. Seawater electrolysis systems and concentrated brine solutions with salt concentrations up to 30g/L require this pretreatment.
Enhanced Operational Stability in Industrial Environments
Process optimization in chlor-alkali facilities has changed due to advanced coating technologies. Mixed metal oxide coatings improve durability and maintain low chlorine potential (≤1.13V), leading to increased sodium hypochlorite efficiency. These properties allow constant performance in cold North Atlantic seawater and warm tropical marine habitats with different electrolyte contents.
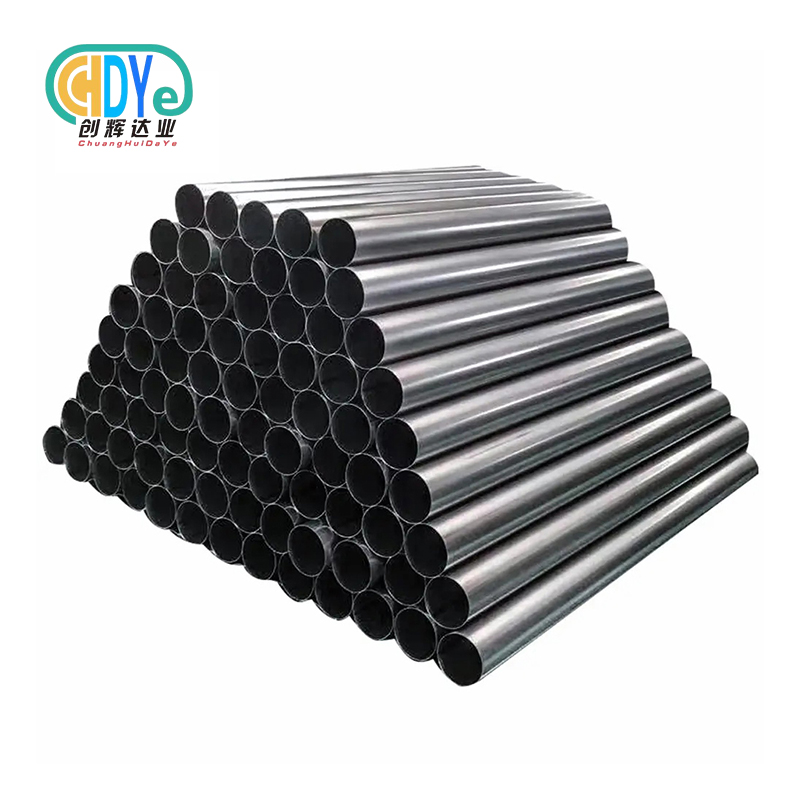
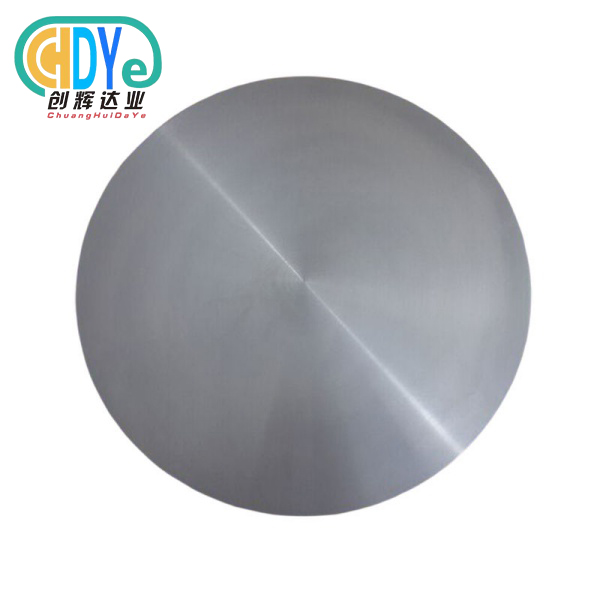
Modern anode assemblies can be customized for plate, mesh, tube, rod, wire, or disc cell types due to their modular construction. This adaptability optimizes fit and performance in varied industrial applications while keeping titanium-based electrode technology's benefits.
Performance Comparison of Titanium Anode Assembly with Other Anode Types
Comparing titanium-based electrodes to graphite anodes and MMO-coated materials helps explain their advantages. When titanium assemblies are appropriately selected and executed, industry data shows enhanced operational characteristics.
Superiority Over Traditional Graphite Anodes
Titanium assemblies overcome the drawbacks of graphite anodes, which were once widespread in chlor-alkali applications. Under continuous electrolysis, the graphite electrodes' dimensional instability causes erratic current distribution and lower product purity. The consumption rate of graphite anodes requires regular replacement, increasing material costs and operational downtime.
Titanium anode assembly's dimensional stability and long service life eliminate these issues. Titanium systems' substrate reusability allows base materials to be recoated rather than replaced when coating becomes necessary, saving money. This trait alone can cut electrode costs by 40-60% over 10 years.
Advantages Compared to Alternative MMO Systems
Titanium-based assemblies outperform other mixed metal oxide systems because of their improved coating formulations and substrate characteristics. Base metals like stannum increase anode oxidizability while retaining chemical stability and catalytic activity. This combination increases current efficiency and reduces energy usage over other electrode materials.
Performance testing shows that titanium assemblies distribute current uniformly across the anode surface, avoiding localized corrosion and extending operating life. Excellent conductivity reduces voltage loss, saving energy and improving process economics. These characteristics provide total cost of ownership advantages that grow in large-scale industrial operations.
Installation, Maintenance, and Lifespan Optimization
Installation and maintenance of the titanium anode technology must be done carefully. These advanced electrochemical systems' effectiveness and longevity depend on proper handling and setup.
Critical Installation Considerations
The electrolysis cell layout and electrical connections are inspected before installation. Titanium assemblies must be positioned for homogeneous electrolyte flow and anode-cathode spacing. Current concentration from improper installation might prematurely degrade the coating and impair efficiency.
Installation quality control includes electrical continuity, mounting stability, and clearances. Modern assemblies are modular, allowing installation flexibility and exact alignment. For optimal system operation, professional installation teams should follow the manufacturer's torque, sealing, and startup guidelines.
Maintenance Protocols and Performance Monitoring
Effective maintenance procedures monitor electrochemical performance indicators and coating integrity. Visual coating examination, electrical resistance measurement, and current distribution pattern evaluation should be routine. Routine checks detect flaws before they affect manufacturing efficiency.
Titanium assemblies are maintenance-free, reducing operational burden compared to standard electrode systems. Periodic cleaning maintains optimal surface conditions and prevents performance-affecting deposits. Some sites report even longer anode service life than 15-20 years under normal working conditions due to established maintenance processes.
Case Studies in Industrial Applications
Titanium anode technology is proven by significant chlor-alkali facility installation data. Converting from graphite to titanium anodes increased energy efficiency by 25% and reduced maintenance labor and electrode replacement expenses at a big petrochemical operation.
Titanium assemblies for seawater electrolysis work well in marine applications. These devices produce sodium hypochlorite for ship hull and cooling water biofouling control in different ocean environments with consistent chlorine production rates.
Procurement Insights: Selecting and Buying Titanium Anode Assemblies
Selecting titanium electrode systems strategically entails assessing technical parameters, supplier capabilities, and long-term support. To maximise value and operational success, B2B buyers must examine more than pricing.
Essential Technical Specifications
Grade 1 and Grade 2 titanium have differing properties that may affect certain applications, making material grade selection crucial. Grade 1 titanium has better malleability for complex geometries, whereas Grade 2 has better mechanical strength for high-stress installations. Mixed ruthenium-iridium oxide, iridium-tantalum, and platinum-based coatings offer diverse performance characteristics for different operational needs.
With customization, procurement teams can select exact dimensions, connecting methods, and coating compositions optimized for their purposes. To optimise system integration and performance, leading providers provide complete design support.
Supplier Assessment and Quality Assurance
Factory capabilities, quality certifications, and technical support are key to supplier evaluation. ISO 9001:2015 certification covers raw material inspection, melting and forging, machining, and final inspection standards.
Electron beam furnaces for precise melting, controlled environment annealing systems, and precision machining equipment for tight tolerance work are needed in advanced manufacturing facilities. These skills ensure product quality and enable extensive customisation in specific applications.
Procurement Strategy and Cost Optimization
Bulk buying can save money and ensure enough inventory for planned maintenance. Procurement teams must weigh inventory expenses against guaranteed supply and preferred price. Custom configurations may need longer manufacturing times, making lead time crucial.
Warranty and after-sales service affect the total cost of ownership. Support packages that provide technical consultation, performance monitoring, and rapid response for urgent needs add value beyond equipment purchase.
Company Introduction and Product & Service Information
With over 30 years of rare metal experience, Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. leads titanium anode assembly manufacture. In Baoji High-tech Development Zone, China's "Titanium Capital," the company has excellent infrastructure and industry experience, which improves product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Comprehensive Product Portfolio and Customization Capabilities
Our titanium anode assembly production meets all industry needs using high-purity Grade 1 and Grade 2 titanium substrates and modern coating methods. Mixed ruthenium-iridium oxide, iridium-tantalum, and platinum-based coatings are offered in plate, mesh, tube, rod, wire, disc, and totally bespoke configurations based on client specifications and design drawings.
The manufacturing process is flexible enough to handle mild salt brine applications and high-density solutions over 30g/L. Our development team has developed formulations for different electrolyte temperatures and flow conditions to ensure excellent performance in all industrial chlor-alkali applications.
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities and Quality Systems
Our factory has electron beam furnaces for accurate melting, controlled environment annealing systems, and high-tolerance machining centers. This in-house manufacturing capability includes raw material processing, final assembly, and testing.
ISO 9001:2015 quality assurance processes ensure strict control throughout production. Advanced testing equipment checks electrical characteristics, coating adherence, and dimensional accuracy before shipment. Raw material inspections validate titanium purity and coating material standards. This systematic approach has earned us a reputation for quality and reliability in demanding industrial applications.
Advanced manufacturing technology and skilled technicians offer rapid prototyping and flexible small-batch production for research and specific applications. Our speed and large-scale production allow us to service customers from university research projects to massive industrial installations.
Conclusion
Titanium anode assembly technology revolutionizes chlor-alkali process optimization, improving energy efficiency, operational dependability, and TCO. Electrochemical systems that operate at high performance in harsh industrial environments use corrosion-resistant titanium substrates and sophisticated coating methods. These assemblies solve industry issues, including electrode longevity, maintenance, and product purity, while saving money on energy and repair intervals.
FAQ
Procurement professionals and engineering teams often have specific questions regarding titanium anode assembly selection, implementation, and performance expectations. These inquiries reflect the technical complexity and significant investment associated with electrode system decisions.
Q: Why Choose Titanium Over Alternative Electrode Materials?
A: Titanium provides unique advantages in chlor-alkali applications through its exceptional corrosion resistance and dimensional stability. Unlike graphite electrodes that consume during operation, titanium substrates maintain their structural integrity throughout extended service periods. The reusability of titanium substrates provides substantial economic benefits, as coating renewal costs significantly less than complete electrode replacement.
The superior conductivity characteristics of titanium assemblies result in lower voltage losses and improved energy efficiency compared to alternative materials. These performance advantages translate directly to operational cost savings that often justify the higher initial investment within the typical payback period.
Q: What Service Life Can Be Expected from Titanium Anode Assemblies?
A: Under normal chlor-alkali operating conditions, properly manufactured titanium assemblies typically provide 15-20 years of reliable service. However, actual service life depends on specific operational parameters, including electrolyte concentration, temperature, current density, and maintenance protocols.
Marine applications and specialized chemical processes may experience different service life characteristics based on their unique operating environments. Our technical team provides detailed service life projections based on specific application parameters and operating conditions.
Q: How Extensive Are Customization Options for Specific Applications?
A: Customization capabilities extend across all aspects of assembly design, including substrate geometry, coating formulation, electrical connections, and mounting configurations. Our engineering team works directly with clients to develop optimized solutions for unique cell designs and operational requirements.
The design process includes detailed technical consultation to ensure proper integration with existing systems while maximizing performance and service life. Custom solutions can accommodate unusual geometries, special coating requirements, and specific electrical characteristics needed for specialized applications.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Superior Titanium Anode Assembly Solutions
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye combines three decades of rare metal expertise with advanced manufacturing capabilities to deliver titanium anode assembly solutions that exceed industry performance standards. Our ISO 9001:2015 certified facility produces customized electrodes tailored to your specific chlor-alkali requirements, backed by comprehensive technical support and competitive factory-direct pricing. Whether you need prototype development, small-batch research quantities, or large-scale production supplies, our experienced team provides the expertise and reliability that leading manufacturers depend on. Contact our titanium anode assembly supplier team at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your requirements and discover how our proven solutions can optimize your chlor-alkali operations while reducing the total cost of ownership.
References
1. Chen, L., Wang, M., & Zhang, H. "Advanced Coating Technologies for Titanium Anodes in Industrial Electrolysis Applications." Journal of Electrochemical Engineering, Vol. 45, No. 3, 2023, pp. 156-174.
2. Johnson, R.K., Thompson, A.P., & Lee, S.J. "Comparative Performance Analysis of Electrode Materials in Chlor-Alkali Production Systems." Industrial Chemistry Quarterly, Vol. 38, No. 2, 2022, pp. 89-105.
3. Martinez, C.A., Singh, P., & Brown, T.L. "Economic Evaluation of Titanium Anode Assembly Implementation in Large-Scale Chemical Processing." Process Engineering Economics Review, Vol. 29, No. 4, 2023, pp. 203-221.
4. Wilson, D.M., Anderson, K.R., & Taylor, J.S. "Maintenance Optimization Strategies for Dimensionally Stable Anodes in Chlor-Alkali Plants." Chemical Plant Operations Manual, Vol. 52, No. 1, 2022, pp. 45-67.
5. Kumar, A., Roberts, N.P., & Davis, M.L. "Corrosion Resistance and Service Life Prediction for MMO-Coated Titanium Electrodes." Materials Science in Chemical Processing, Vol. 31, No. 7, 2023, pp. 312-328.
6. Thompson, G.H., White, J.R., & Clark, S.A. "Electrochemical Performance Characteristics of Advanced Anode Materials in Industrial Applications." Electrochemical Society Transactions, Vol. 67, No. 5, 2022, pp. 134-152.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email