- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
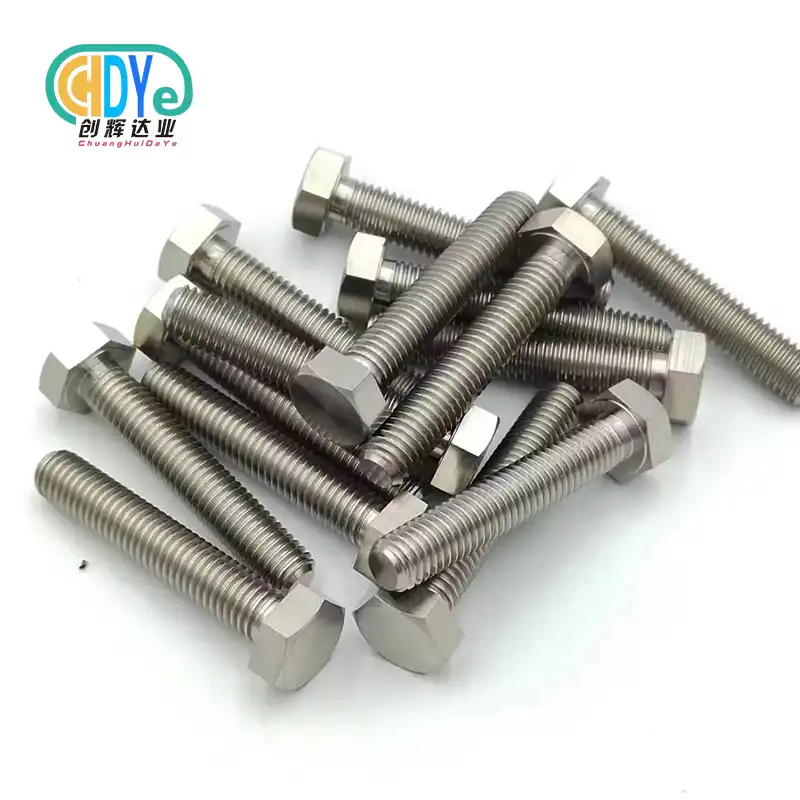
What Standards Do Titanium Fasteners Meet (ISO/ASTM/DIN)?
ISO, ASTM, Noise, and GB measures are met by titanium fasteners. These broad benchmarks direct fabric composition, mechanical qualities, dimensional resistances, and testing to guarantee worldwide application quality and execution. Each standard system indicates chemical composition, ductile quality, erosion resistance, and fabricating forms, permitting producers and procurement experts to indicate Gr1, Gr2, and Gr5 titanium combinations for different mechanical applications.

Introduction
Due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight, titanium fasteners are vital to worldwide B2B industries. These fasteners must fulfill strict worldwide standards for quality, safety, and performance in aeronautical, automotive, and industrial engineering applications. This reference covers ISO, ASTM, and DIN titanium fastener standards in detail, helping procurement professionals and engineers make informed selections that comply with international standards and industry best practices. In modern production, fastening solutions must survive harsh conditions and retain structural integrity over long periods. The aircraft sector needs fasteners that work at -250°C to 600°C, while chemical processing plants need components that resist saltwater, acids, and chlorine compounds. These tough requirements have led to detailed international standards that ensure titanium fastening hardware performs consistently regardless of production origin or application environment.
Understanding Titanium Fasteners and Their Industry Standards
Titanium alloy fasteners provide a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Bolts, nuts, screws, washers, threaded rods, studs, and anchors are used in circumstances where steel fasteners are too heavy or environmentally hazardous.
Material Properties and Performance Characteristics
Titanium alloy fasteners are essential in many industries due to their unique features. At 4.51 g/cm³, titanium fastening hardware is 40% lighter than steel and offers greater strength, reducing assembly weight without affecting mechanical performance. This weight advantage is especially useful in aerospace applications where every gram affects fuel economy and payload.
The natural oxide layer of titanium resists corrosion, making it reliable in maritime, chemical processing, and other corrosive settings where standard fasteners would deteriorate quickly. Its non-magnetic qualities make it excellent for precise instruments and electronic applications where magnetic interference could degrade system performance.
Standards Organizations and Their Global Impact
International standards groups help standardize titanium fastening hardware. The ISO creates worldwide standards to ease international trade and product compatibility. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) develops testing methods and material specifications used in North America and elsewhere. DIN sets European standards for precise engineering and dimensional accuracy.
These standards frameworks assure uniformity in material composition, mechanical qualities, and manufacturing processes, allowing procurement managers to express requirements confidently and vendors to confirm compliance through standardized testing and certification.
Core Standards Governing Titanium Fasteners
Titanium fastener specification, testing, and quality assurance are covered by international standards. Understand these standards to make educated buying decisions and optimize application performance.
ISO Standards for Titanium Fasteners
ISO standards define titanium fastener composition and performance worldwide. The ISO 5832 series specifies chemical composition and mechanical properties for medical titanium alloys. ISO 3506 covers corrosion-resistant stainless steel, related alloys, and fixing titanium grades.
These standards set specific titanium grade chemical composition ranges, assuring material consistency between manufacturers. For strength, Grade 2 allows somewhat higher interstitial element concentration than Grade 1 (commercially pure titanium), which has 0.18% oxygen, 0.20% iron, and 0.03% nitrogen. Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) has greater strength for structural applications due to aluminum and vanadium alloying.
ASTM Standards and Testing Requirements
ASTM standards detail titanium fastener materials and testing. ASTM F468 covers titanium bolts, hex cap screws, and studs for general corrosion service, while ASTM F467 covers titanium and titanium alloy nuts. These standards set chemical composition limitations, mechanical qualities, and dimensional tolerances for consistent performance.
ASTM tests include tensile strength, stress rupture, and corrosion resistance. Grade 2 titanium requires 345 MPa minimum ultimate tensile strength, whereas Grade 5 requires 895 MPa. These stringent testing processes ensure fasteners operate well in service.
DIN Standards and European Specifications
DIN standards stress precision manufacturing and dimensional correctness for the European industry. Flange head bolts with certain dimensional tolerances are covered by DIN 6921, whereas other DIN specifications cover fastener geometries and threading.
German and European precise engineering traditions lead to tighter dimensional tolerances in European standards than in other international standards. Automated production and high-precision applications require a consistent fit and assembly.
Comparing Titanium Fastener Standards - What Buyers Should Know?
Understanding differences between key international standards helps procurement professionals choose acceptable specifications for individual applications while maintaining quality management system compatibility.
Testing Methodology Variations
Titanium fastener performance is tested differently by different standards organizations. ASTM standards emphasize regulated laboratory tensile, yield, and elongation testing. ISO standards commonly include corrosion testing to imitate real-world service situations.
DIN standards emphasize dimensional accuracy and threading precision, reflecting European manufacturing traditions that value fit and assembly. These frameworks offer complementary views on fastener quality, addressing specific performance and reliability issues.
Grade Classifications and Material Selection
Titanium grade selection affects fastener performance and cost. Grade 1 titanium is good for non-structural applications due to its corrosion resistance and formability, but low strength. Grade 2 is strong and corrosion-resistant, making it appropriate for general industrial applications.
Aluminum and vanadium alloying make Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) strong enough for aerospace and high-performance automotive applications. Procurement strategy must account for greater material costs and more complex manufacturing requirements due to increased strength.
Performance Comparison with Alternative Materials
Titanium fasteners outperform stainless steel in corrosive and weight-critical situations. Longer service life and lower maintenance costs make titanium a better total cost of ownership, especially in maritime and chemical processing applications.
Titanium fasteners are biocompatible and non-magnetic, making them ideal for medical device applications that require material safety.
Procurement Insights: Sourcing Titanium Fasteners that Meet Standards
Supplier evaluation and quality verification are necessary to buy standards-compliant titanium fasteners.
Supplier Certification and Quality Management
Supplier qualification requires ISO 9001:2015 quality management system certification and product standard compliance. Material test reports, dimensional inspection records, and traceability information linking completed products to raw materials are kept by reliable suppliers.
Quality management systems should include raw material inspection, manufacturing process control, and final inspection for standard compliance. AS9100 for aerospace and ISO 13485 for medical device manufacture are common certifications for advanced vendors.
Custom Manufacturing and Lead Time Considerations
Due to sophisticated processing and quality testing, custom titanium fastener manufacturing takes longer than regular hardware. Custom requirements may require larger order quantities, requiring demand forecasting and inventory management.
Suppliers with extensive machining skills can meet M2 to M25 and beyond criteria with unique lengths and threading. Advanced manufacturing facilities using electron beam welding, precision machining centers, and heat treatment equipment can produce complicated fastener shapes with tight dimensional tolerances.
Documentation and Traceability Requirements
Material test certifications, dimensional inspection reports, and traceability records linking completed goods to raw materials are essential paperwork. These documents are crucial for aeronautical, medical, and nuclear quality audits and regulatory compliance.
Packaging in protective cartons or specialized containers protects products during delivery, while visible labeling aids inventory management and quality control.
Trusted Partner for Titanium Fasteners
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of standards-compliant titanium fasteners with over 30 years of rare metal industry experience and cutting-edge manufacturing. Our facility is near raw material sources and has good transportation infrastructure in Baoji High-tech Development Zone, China's "Titanium Capital."
Comprehensive Product Portfolio and Manufacturing Capabilities
We make bolts, nuts, screws, washers, threaded rods, studs, and anchors from Gr1, Gr2, and Gr5 titanium alloys. Standard standards are M2 to M25, with bespoke lengths available for specific applications.
Fasteners fulfilling ISO, ASTM, DIN, and GB requirements are made using electron beam furnaces, precision machining centers, and specialist rolling mills. During manufacturing, our annealing furnaces and heat treatment facilities maintain ideal mechanical qualities and dimensional stability.
Quality Assurance and Certification
ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System Certification shows our dedication to production-wide quality control. Quality methods include raw material inspection, melting and forging process monitoring, precision machining verification, and packaging inspection.
All shipments include material test certifications for chemical composition and mechanical property verification. Dimensional inspection reports verify tolerances, while traceability documentation links final items to raw materials for supply chain transparency.
Technical Support and Customer Service
Our expert technical staff helps with material grade selection, dimensional specification optimization, and bespoke fastener design. Engineering consultancy helps customers balance performance, cost, and industry norms.
Flexible packaging meets international shipping needs while protecting product integrity. Customer service helps streamline the procurement process from inquiry to delivery and after-sales support.
Conclusion
Understanding titanium fastener international standards for titanium fasteners helps buyers balance performance and cost. ISO, ASTM, and DIN standards ensure worldwide supply chain quality and performance. Successful titanium fastener procurement requires supplier selection, quality verification, and documentation inspection. Titanium alloy fasteners are essential for aircraft, marine, chemical processing, and medical device applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and non-magnetic qualities. Maintaining international standards provides reliable performance and facilitates worldwide trade and regulatory compliance.
FAQ
Q: What are the main differences between ASTM and ISO titanium fastener standards?
A: ASTM and ISO standards differ primarily in testing methodologies and regional focus. ASTM standards emphasize comprehensive mechanical testing protocols widely used in North American markets, while ISO standards provide globally applicable specifications with emphasis on international trade facilitation. Both frameworks address similar performance requirements but may specify different testing procedures or acceptance criteria for equivalent fastener grades.
Q: How can I verify that titanium fasteners meet DIN standard requirements?
A: Verification of DIN standard compliance requires review of supplier quality documentation, including dimensional inspection reports, material test certificates, and manufacturing process records. Qualified suppliers provide comprehensive certification packages demonstrating adherence to specified DIN requirements, including dimensional tolerances, threading precision, and material composition limits.
Q: Which titanium grade is recommended for aerospace applications?
A: Aerospace applications typically utilize Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) titanium for structural fasteners due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and proven performance characteristics. Grade 2 titanium may be suitable for non-structural applications where corrosion resistance is the primary concern. Grade selection depends on specific stress requirements, environmental conditions, and weight constraints within the particular aircraft system.
Q: What documentation should accompany certified titanium fasteners?
A: Certified titanium fasteners should include material test certificates showing chemical composition analysis and mechanical property verification, dimensional inspection reports confirming compliance with specified tolerances, and traceability documentation linking finished products to raw material sources. Additional certifications may be required for specific industries, such as aerospace (AS9100) or medical devices (ISO 13485).
Contact Chuanghui Daye for Premium Titanium Fastener Solutions
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye Metal Material Co., Ltd. offers comprehensive titanium fastener manufacturing services backed by ISO 9001:2015 certification and over 30 years of specialized experience. Our advanced production facility in China's Titanium Capital produces fasteners meeting ISO, ASTM, and DIN standards with complete traceability documentation. Contact our technical team at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific requirements and receive detailed quotations for custom or standard titanium fastener specifications.
References
1. American Society for Testing and Materials. "ASTM F468-19: Standard Specification for Nonmagnetic Titanium Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and Studs for General Corrosion Service." ASTM International, 2019.
2. International Organization for Standardization. "ISO 3506-6:2020: Corrosion-resistant stainless steel fasteners - Part 6: General rules for the selection of stainless steels and nickel alloys for fasteners." ISO Publications, 2020.
3. Deutsches Institut für Normung. "DIN 6921:2016: Hexagon head bolts with flange - Product grades A and B." DIN Standards, 2016.
4. Boyer, Rodney R. "An Overview on the Use of Titanium in the Aerospace Industry." Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 213, no. 1-2, 1996, pp. 103-114.
5. Donachie, Matthew J. "Titanium: A Technical Guide, Second Edition." ASM International Materials Park, 2000.
6. Peters, M., et al. "Titanium Alloys for Aerospace Applications." Advanced Engineering Materials, vol. 5, no. 6, 2003, pp. 419-427.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email
_1760924769851.jpg)