- English
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Greek
- German
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
What Sizes of Titanium Baskets Are Available for Electroplating?
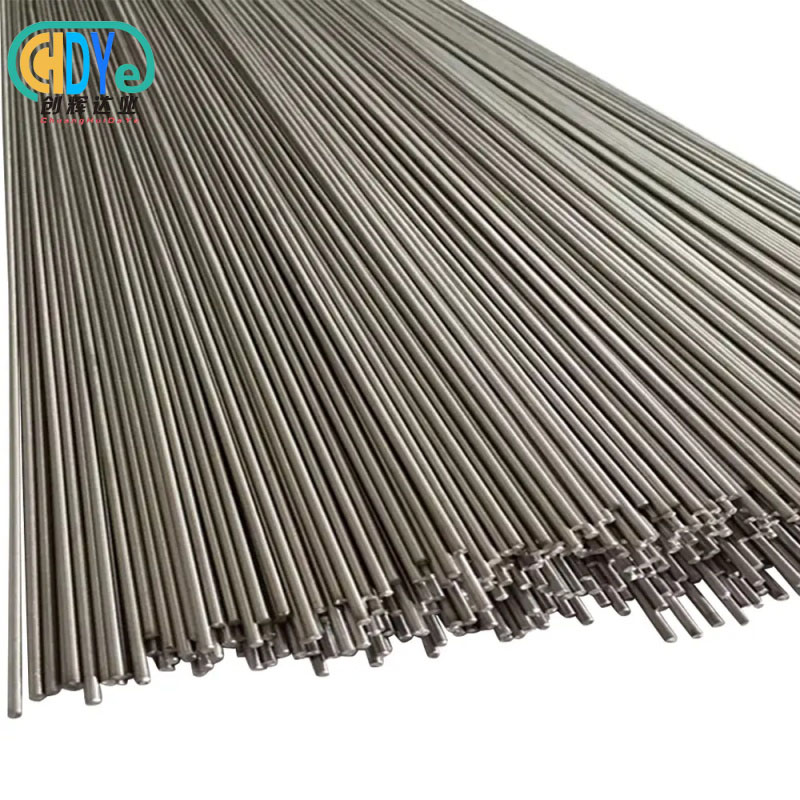
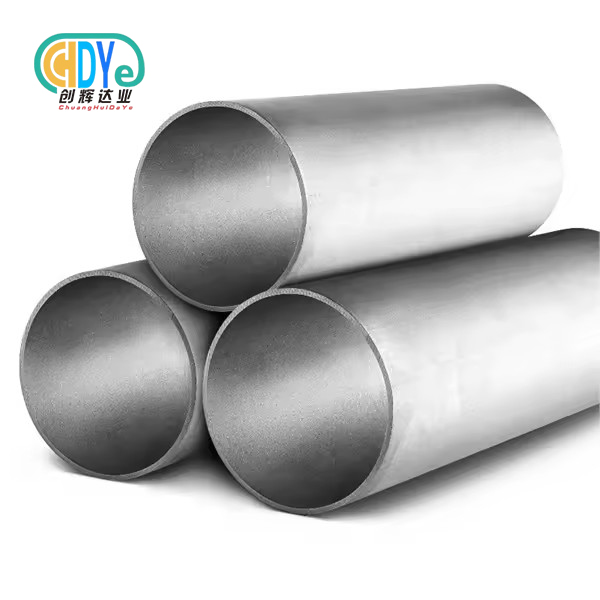
Titanium basket sizes for electroplating range from 50x50x25mm laboratory units to 600x400x300mm industrial containers. Small (100x100x50mm to 200x150x100mm), medium (250x200x120mm to 400x300x200mm), and large-capacity baskets are standard. Titanium mesh containers can be custom-sized to fit electroplating bath dimensions, component geometries, and production volumes for maximum current distribution and processing efficiency in many industrial applications.
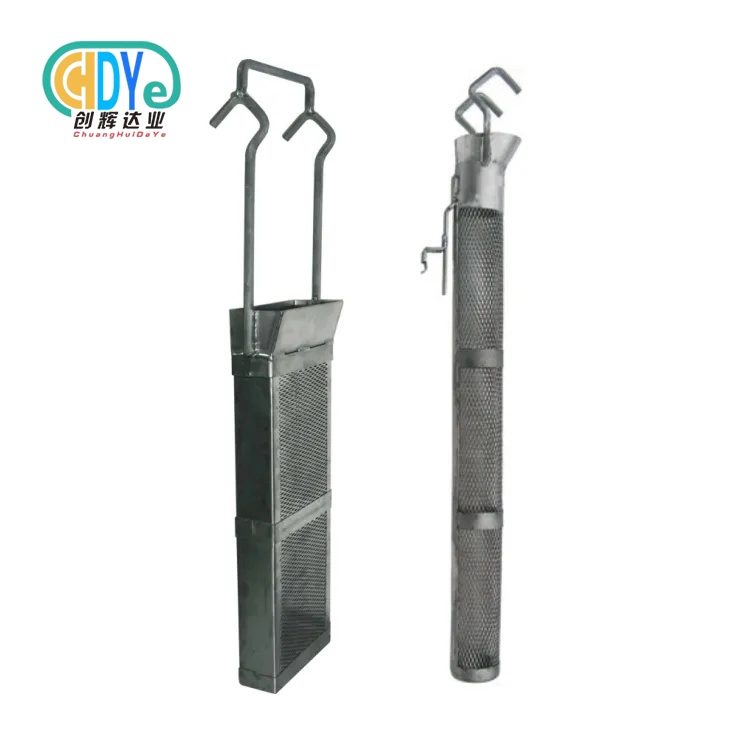

Understanding Titanium Basket Sizes for Electroplating
Container dimensions must be precisely controlled for electroplating to ensure coating quality and efficiency. Basket size affects electroplating performance beyond volume, including current density distribution, component spacing, and electrolyte circulation patterns.
Standard Dimensional Categories
Three main sizes of titanium basket containers are made for different manufacturing scales. Precision applications requiring component spacing and current control use 100x100x50mm and 200x150x100mm baskets. These tiny devices thrive in medical device plating, jewelry finishing, and electronics manufacturing, where electrochemical parameters must be monitored for part consistency.
General industrial electroplating is most versatile in 250x200x120mm to 400x300x200mm configurations. These dimensions accommodate automotive components, hardware assembly, and mid-scale manufacturing runs while complying with electroplating tank standards. Balanced proportions allow efficient loading while maintaining electrolyte circulation around components.
450x350x250mm to 600x400x300mm baskets meet heavy industry bulk processing needs. These large containers handle huge components, high-volume production batches, and specialized assemblies where traditional sizing fails. These proportions require advanced welding and reinforced frame designs to withstand operational loads.
Custom Sizing Considerations
Custom dimensioning solves operational issues that off-the-shelf alternatives cannot. Basket proportions are frequently determined by component geometry to maximize loading efficiency and consistent current exposure across surfaces. Bath tank dimensions may need non-standard basket arrangements to increase capacity and allow automated handling system clearances.
Customization requires extensive examination of component qualities, production volume, and infrastructural constraints. Engineers consider current density, agitation patterns, and maintenance access to create appropriate dimensional specifications that improve process performance.
Key Size Variations Based on Electroplating Applications
Basket sizing must be tailored to each industry's operating needs and quality standards. Understanding these application-specific requirements helps procurement managers choose configurations that improve process efficiency and coating quality.
Precision Electronics and Medical Device Applications
The electronics and medical device industries require precise dimensions and surface finishes. These industries use titanium containers between 75x75x40mm and 180x120x80mm to protect fragile components that need homogeneous coating. Smaller dimensions provide accurate current density control and accommodate complex electronic assembly and medical implant designs.
Medical applications demand biocompatibility, while sensitive electronic components require chemical inertness. Grade 1 and 2 titanium construction provides both. Electrolyte penetration is optimized by the mesh plate architecture, which supports lightweight components that may be displaced during processing.
Automotive and Industrial Hardware Processing
Strong basket designs are needed for automotive component electroplating due to part shapes and manufacturing quantities. Standards for this sector range from 300x250x150mm to 500x400x250mm, accommodating small fasteners to large brake components and decorative trim.
These applications prioritize frame plate durability and dimensional stability during temperature cycling and chemical exposure. Joint integrity can endure mechanical pressures from automated handling systems and high-throughput manufacturing environments with argon arc welding.
Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing
Space applications require the highest basket construction and dimensional precision. Precision instrumentation components sit in 200x150x100mm containers, while structural assemblies needing specific coatings are 400x350x200mm. This industry requires traceability documentation and aircraft material specifications due to strict quality standards.
The titanium mesh plate, frame plate, and hook assemblies provide mechanical durability for important aerospace applications and chemical resistance for new coating chemistries in this challenging environment.
Manufacturing Process Impact on Basket Size Availability
The fabrication process affects the titanium basket's dimensional accuracy and size range. Advanced production methods allow fine dimension control while maintaining structural integrity for long-term electroplating.
Argon Arc Welding Advantages
Argon arc welding is best for titanium basket manufacturing because it preserves material purity and creates robust, corrosion-resistant joints. Inert atmosphere welding prevents oxidation and ensures weld zones have the same corrosion resistance as titanium.
Precision from argon arc welding allows producers to maintain tight dimensional tolerances across all sizes. Optimizing welding parameters for basket dimensions ensures that small precision units and big industrial containers receive heat input levels that protect material qualities and achieve robust joint strength.
Quality Control Throughout Size Ranges
Comprehensive quality control techniques that handle dimensional category problems are needed to ensure manufacturing uniformity across size ranges. Small baskets require precise assembly, while bigger units need structural analysis to withstand operational loads.
ISO 9001:2015 accreditation assures quality management systems include raw material inspection to final packaging. This systematic methodology ensures dimensional correctness and structural integrity regardless of basket size or configuration complexity.
Customization Capabilities and Limitations
Beyond dimensional scaling, custom sizing includes compartmentalization, integrated handling systems, and application-specific design characteristics. Titanium fabrication versatility allows producers to meet unique operational requirements while keeping the performance attributes that make titanium containers perfect for electroplating.
Custom configurations take 2-4 weeks to manufacture, depending on intricacy and size. This timeline shows the thorough engineering study and fabrication planning needed to achieve dimensions and performance requirements for unique solutions.
Comparing Titanium Basket Sizes with Alternatives for Electroplating
Material selection greatly affects size availability and performance across dimensions. Understanding these trade-offs helps choose electroplating containers.
Stainless Steel Comparison Across Size Ranges
Stainless steel baskets are strong and useful in large applications with heavy structural stresses. Stainless steel construction's weight penalty makes basket handling harder as the basket size increases. A 500x400x250mm stainless steel container weighs 40-50% more than a titanium version, affecting operator ergonomics and automation system needs.
Another important difference aspect is corrosion resistance, which rises with basket size. Larger containers have more corrosion-prone surfaces, making titanium's chemical resistance advantageous in harsh electroplating conditions.
Plastic Alternative Limitations
Plastic baskets have structural integrity and temperature resistance issues as the size increases. Plastic containers may work for small-scale lab applications, but industrial-scale processes require dimensional stability under load.
Plastics' chemical compatibility limits their use in industrial electroplating's pH ranges and chemical compositions. These restrictions increase with container size due to chemical exposure and mechanical strains in larger operations.
Cost-Benefit Analysis by Size Category
Titanium's value proposition rises with basket size because of its lower weight, durability, and corrosion resistance. In tiny applications, initial investment prices may benefit alternative materials, but total cost of ownership calculations favor titanium for medium and large containers.
Titanium construction's extended service life becomes more essential as basket size increases since replacement costs and downtime climb proportionally with container dimensions. Titanium is a good long-term investment for most industrial electroplating applications due to its economics.
Maintenance and Longevity Tips for Titanium Baskets of Different Sizes
Because each basket size has varied handling needs and operational demands, proper maintenance techniques vary greatly. Understanding these size-specific considerations optimizes service life and performance consistency.
Size-Specific Cleaning Protocols
Ultrasonic cleaning removes debris from complicated mesh structures without disassembly in small baskets. Compact size allows complete immersion in ultrasonic baths and access to specialist cleaning chemistry that larger machines may not be able to use.
Manual cleaning and spray-wash systems for mesh and frame components are needed for medium-sized containers. These baskets' dimensions make cleaning, inspection, and maintenance easy.
The bulk and weight of large containers make cleaning them difficult. These devices frequently have in-place cleaning mechanisms that reduce handling and remove pollution. Large basket cleaning techniques must account for greater surface area and uneven contaminant dispersion over the container volume.
Storage and Handling Considerations
Basket dimensions greatly impact storage needs, affecting facility planning and inventory management. Compact storage for small baskets maximizes space and protects them from damage. Similar-sized units benefit from nested storage, lowering storage footprint and improving access.
Large baskets need dedicated storage that supports them without deforming them. Maintaining dimensional accuracy over long periods requires proper storage fittings, especially for containers approaching the maximum size limits, where structural deflection becomes an issue.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
Maintenance intervals should reflect basket size and usage intensity. Due to higher handling frequencies and loading and unloading damage, small, regularly used baskets may need more frequent examination. Small unit inspection techniques can focus on mesh integrity and connection points.
Due to their higher mechanical stresses, large baskets work on longer cycles and require more structural checks. The maintenance program for large containers should include dimensional verification to ensure that operational loads have not produced permanent deformation that could impact performance.
Conclusion
Titanium basket electroplating sizes range from 50mm laboratory units to 600mm industrial containers. The best size depends on application, component, and operational restrictions. Standard configurations meet most industrial applications, while custom size meets aerospace, medical, electronics, and automotive needs. Using Grade 1 and Grade 2 titanium with argon arc welding ensures dimensional precision and structural integrity across all sizes. Titanium containers outperform stainless steel and plastic in corrosion resistance, weight, and durability, especially as dimensions grow. Titanium baskets are a cost-effective long-term investment for electroplating operations due to size-specific maintenance techniques that maximize service life and performance consistency.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common standard sizes for titanium baskets in electroplating?
A: Standard titanium basket dimensions typically range from 100x100x50mm for small applications to 500x400x300mm for large-scale operations. The most popular medium-sized configurations measure between 250x200x120mm and 350x250x180mm, accommodating the majority of industrial electroplating requirements while maintaining compatibility with standard tank dimensions.
Q: How does basket size affect electroplating quality and efficiency?
A: Basket size directly influences current distribution, component spacing, and electrolyte circulation patterns. Properly sized containers ensure uniform current density across all surfaces while maintaining adequate spacing between components to prevent shadowing effects. Oversized baskets may lead to uneven plating, while undersized containers can create current concentration issues that affect coating quality.
Q:Can titanium baskets be customized to specific dimensional requirements?
A: Custom sizing is readily available for titanium baskets, with manufacturers capable of producing containers tailored to specific component geometries, bath dimensions, and production requirements. Custom fabrication typically involves 2-4 week lead times depending on complexity, with dimensional tolerances maintained through precision argon arc welding techniques.
Q: What size limitations exist for titanium basket manufacturing?
A: Manufacturing capabilities typically accommodate baskets ranging from 25x25x15mm for specialized laboratory applications up to 800x600x400mm for heavy industrial use. Extremely large dimensions may require structural reinforcement and specialized handling features, while very small containers demand precision fabrication techniques to maintain mesh integrity and dimensional accuracy.
Q: How do maintenance requirements differ between small and large titanium baskets?
A: Small baskets benefit from ultrasonic cleaning and compact storage solutions, while large containers require specialized cleaning equipment and dedicated storage fixtures. Inspection intervals vary based on usage patterns and structural loading, with larger baskets requiring more comprehensive dimensional verification to detect potential deformation under operational stresses.
Partner with Chuanghui Daye for Your Titanium Basket Manufacturing Needs
Shaanxi Chuanghui Daye stands as your trusted titanium basket supplier, offering comprehensive sizing solutions from compact precision units to large-scale industrial containers. Our advanced argon arc welding capabilities and ISO 9001:2015 certified quality systems ensure dimensional accuracy across all size ranges. Located in China's Titanium Capital, we leverage over 30 years of rare metal expertise to deliver Grade 1 and Grade 2 titanium baskets with superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity. Contact us at info@chdymetal.com to discuss your specific sizing requirements and receive custom quotes for electroplating applications.
References
1. Chen, L., & Wang, M. (2023). Electroplating Container Design: Size Optimization for Industrial Applications. Journal of Surface Treatment Technology, 45(3), 112-128.
2. Rodriguez, A., & Thompson, K. (2022). Titanium Basket Manufacturing: Dimensional Control and Quality Assurance in Electroplating Equipment. Materials Processing Quarterly, 38(7), 234-251.
3. Singh, R., & Liu, H. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Basket Materials and Sizing in Modern Electroplating Operations. International Electrochemical Review, 67(4), 445-462.
4. Morrison, D., et al. (2022). Standard Dimensions and Custom Sizing for Titanium Electroplating Containers: Industry Best Practices. Surface Engineering Handbook, 15th Edition, 892-915.
5. Yamamoto, T., & Anderson, B. (2023). Size-Dependent Performance Characteristics of Titanium Mesh Baskets in Electroplating Applications. Corrosion Science and Engineering, 41(2), 78-94.
6. Williams, S., & Kumar, P. (2022). Manufacturing Tolerances and Dimensional Accuracy in Titanium Basket Production for Electroplating Industries. Precision Manufacturing Review, 29(6), 167-183.
Learn about our latest products and discounts through SMS or email